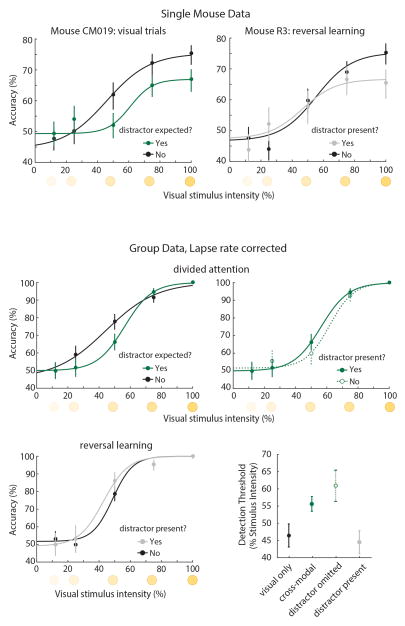
Extended Data Figure 2. Effects of cross-modal divided attention in the mouse.
Top: Single mouse examples of visual detection performance during cross-modal divided attention and reversal learning. Left: Comparison of performance under visual-only (black) and cross-modal (green) conditions. Although neither contained sensory conflict, the mere expectation of one increased detection threshold (≥124 trials per condition). Right: Detection threshold was not impacted by the presence of an auditory distractor during reversal learning (≥90 trials per condition). Bottom: Group data normalized to peak performance (lapse rate), showing that the effects of divided attention on detection threshold were persistent. Bootstrap estimation of visual detection threshold show a similar pattern as data in Figure 1 (error bars are 95% CI).