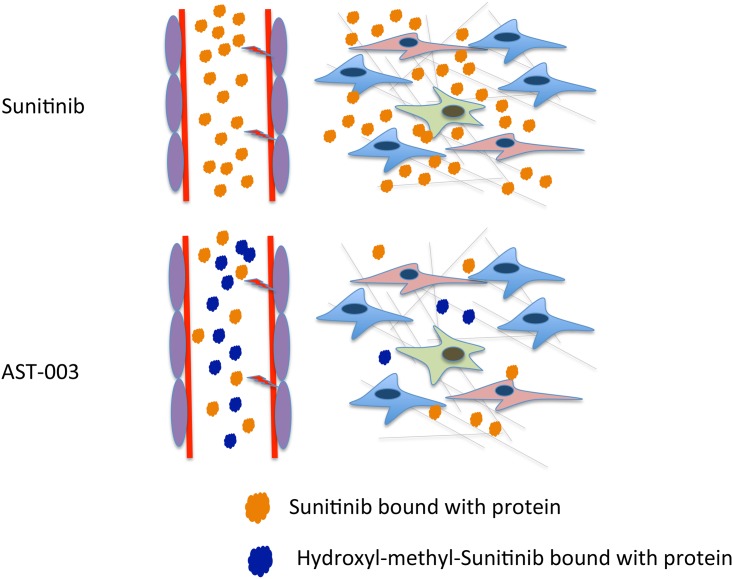
Fig 5. The proposed mechanism of AST-003.
In mice treated with AST-003, the total Sunitinib (Sunitinib plus hydroxyl-methyl-Sunitinib) inhibits angiogenesis and cancer cell growth better than Sunitinib treatment alone because hydroxyl-methyl-Sunitinib kills vascular endothelial cells and cancer cells at a faster rate than Sunitinib. However, as hydroxyl-methyl-Sunitinib is less stable than Sunitinib, the lower sustained tissue concentrations of Sunitinib associated with AST-003 treatment are responsible for the observed reduced toxicity. Thus, AST-003 exhibits higher efficacy and lower systemic toxicity than Sunitinib.