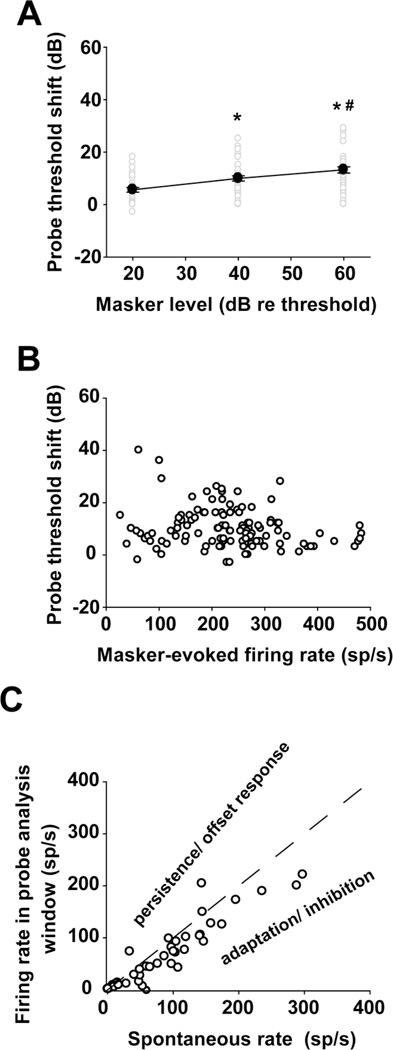
Fig. 5.
Effects of masker level on threshold shifts. a Threshold shift increases with increasing masker level. *: p < 0.05, compared to the lower masker level condition; #: p < 0.05, compared to the intermediate masker level condition. b Threshold shift is independent of masker-evoked firing rate. c Relationship between spontaneous rate and firing rate in the probe analysis window under the masker-alone condition. The dashed line indicates a condition where the firing rate in the probe analysis window equals the spontaneous -activity. In units represented under the line, an adaptation or inhibition-driven mechanism rather than a persistent response to the masker, can account for the unit’s threshold shift in the presence of the masker.