Fig. 1.
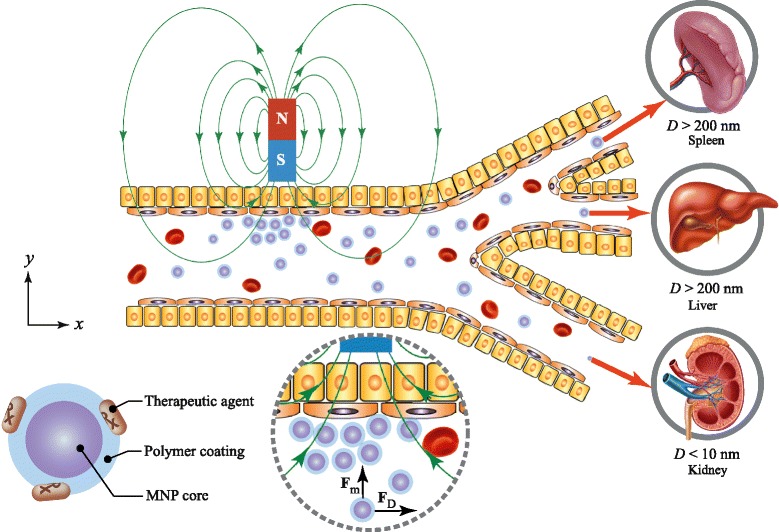
Drug-loaded carrier is typically composed of a magnetic core and a biocompatible coating material. The magnetic core was made from different materials such as Fe3O4, Fe2O3, or Fe. The coating materials are Au, PEG, or SiO2. Based on the biokinetics of particles, a drug carrier ranging from 10–200 nm in diameter is optimal for in vivo delivery, as the small particles (D<10 nm) escape by renal clearance [18] and the large ones (D>200 nm) are sequestered by the reticuloendothelial system of the spleen and liver [18]
