Figure 1.
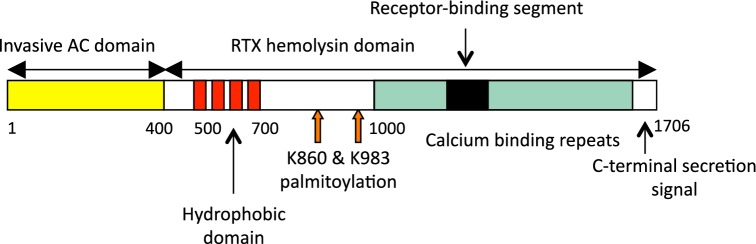
Schematic representation of the CyaA molecule. CyaA is a 1706 residue-long polypeptide that contains an N-terminal adenylate cyclase (AC) enzyme domain (∼400 residues) and a C-terminal pore-forming RTX hemolysin moiety of ∼1300 residues. The RTX hemolysin portion of CyaA itself consists of several functional subdomains. It contains (i) a hydrophobic pore-forming domain, comprising residues 500–700; (ii) an activation domain between residues 800 and 1000, where the posttranslational palmitoylation at two lysine residues (K860 and K983) occurs; (iii) a typical calcium-binding RTX domain, harboring the nonapeptide glycine- and aspartate-rich repeats, which form numerous (∼40) calcium-binding sites and the integrin-binding domain and (iv) the C-terminal secretion signal, respectively.
