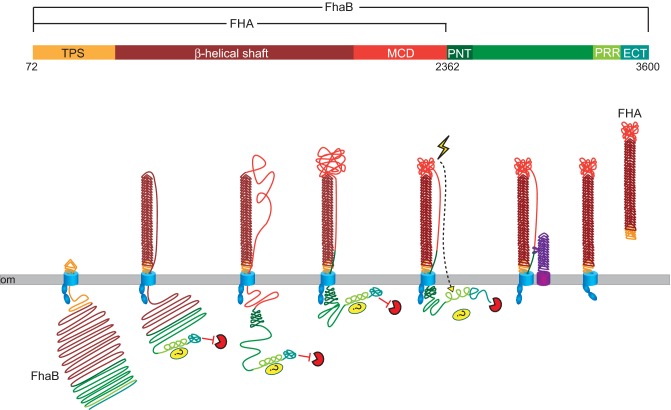
Figure 1.
FHA biogenesis. FhaB is an ∼370 kDa polypeptide. After removal of the 71 aa signal sequence, the TPS domain of FhaB (gold) interacts with the POTRA domains of FhaC (blue), initiating translocation across the outer membrane (om). The N-terminal ∼2500 aa of FhaB fold into a β-helix on the cell surface. The C-terminal proline-rich region (PRR) may interact with a periplasmic protein or protein domain, and the extreme C-terminal domain (ECT) inhibits an unknown protease. The N-terminus of the prodomain (PNT, dark green) prevents translocation of the prodomain across the om. In response to an unknown signal, the ECT releases inhibition of the unknown protease and the prodomain is degraded. FhaB is also processed by the serine protease SphB1 (purple) to form ‘mature’ ∼240 kDa FHA. FHA is released from the cell surface by an unknown mechanism.