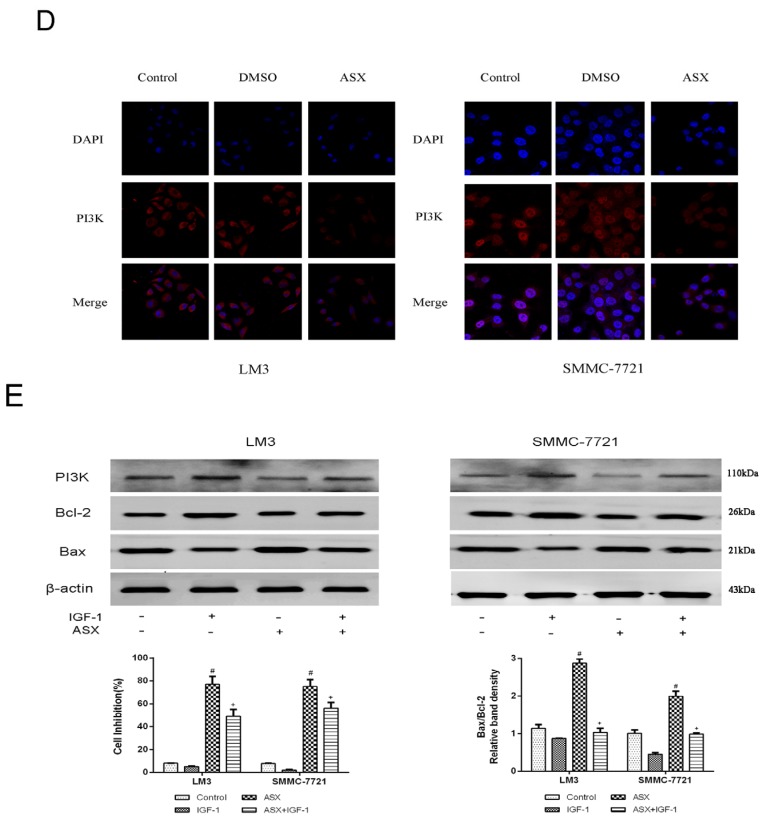
Figure 4.
Effects of ASX on the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway via the reduction of GSK-3β inactivation. (A) The mRNA expression of GSK-3β and β-catenin was determined using real-time PCR (n = 3, *,#,+ p < 0.05 for ASX versus DMSO); (B) The protein levels of GSK-3β, β-catenin and p-GSK-3β were determined by western blotting; (C) The protein levels of PI3K, ERK, p-ERK, Akt, and p-Akt were determined by western blotting. The ratio of p-ERK and ERK, p-Akt, and Akt were calculated using the Odyssey two-color infrared laser imaging system (n = 4, *,#,+ p < 0.05 for ASX versus DMSO); (D) The expression of PI3K was assessed by immunofluorescence after ASX treatment. The red fluorescence showed that PI3K and the nuclear region was dyed blue by 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Magnification 630×; (E) The protein levels of PI3K, Bax, Bcl-2, and β-actin in LM3 and SMMC-7721 were determined by western blotting. The relative band intensities of Bcl-2 and Bax were calculated using the Odyssey two-color infrared laser imaging system. The inhibition rates were evaluated by CCK8 (n = 4, #p < 0.05 for ASX versus Control, + p < 0.05 for ASX + IGF-1 versus ASX).