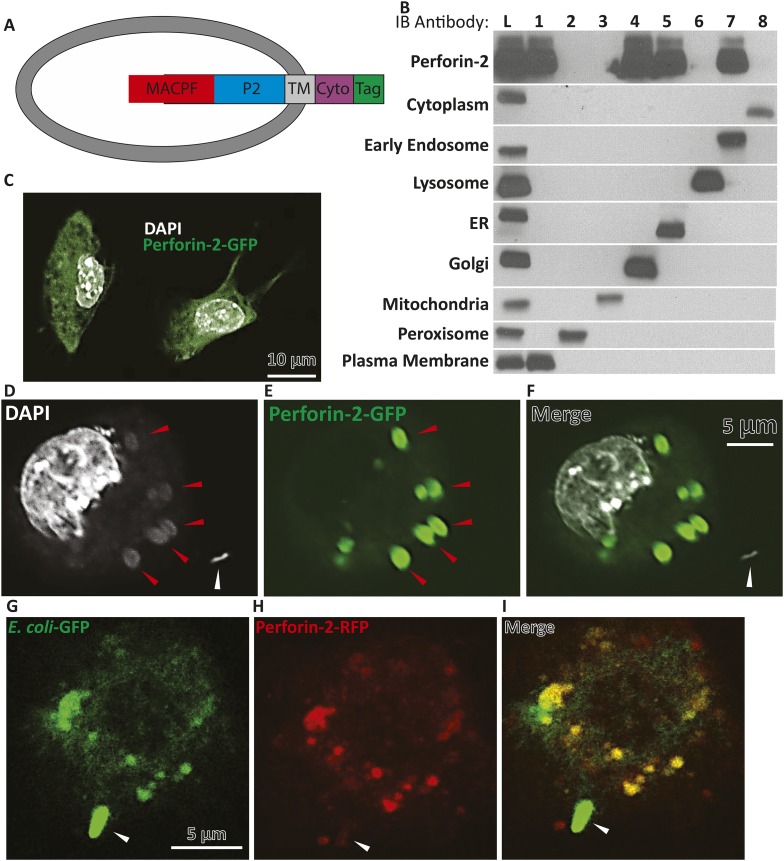
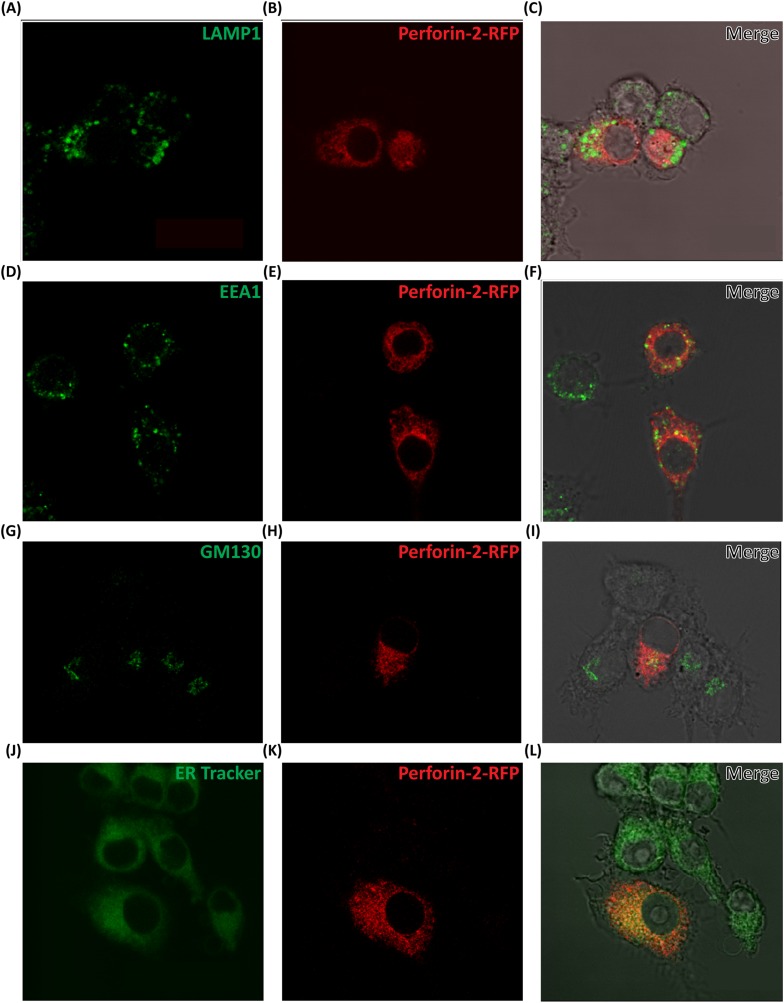
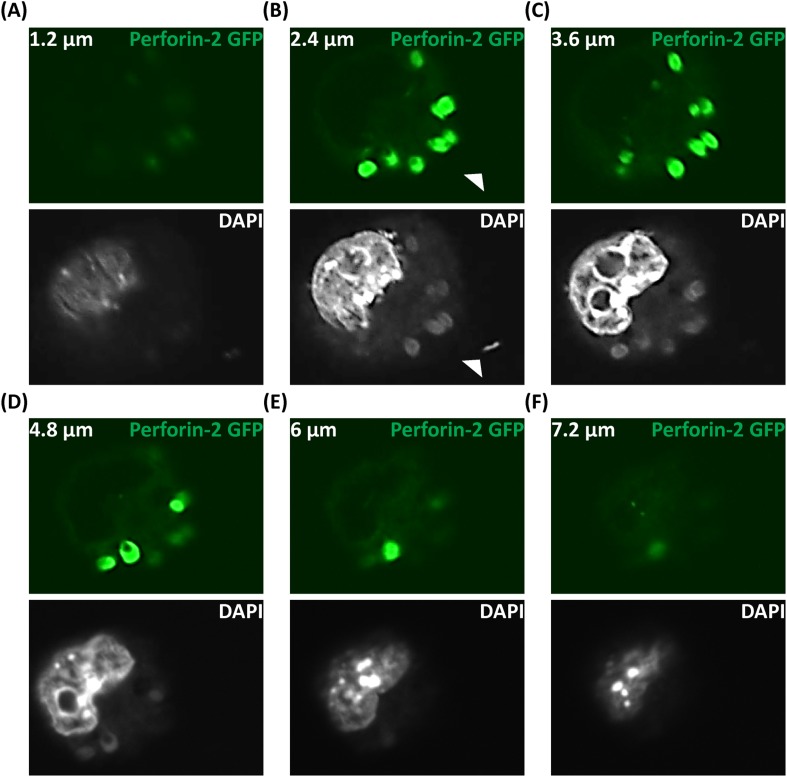
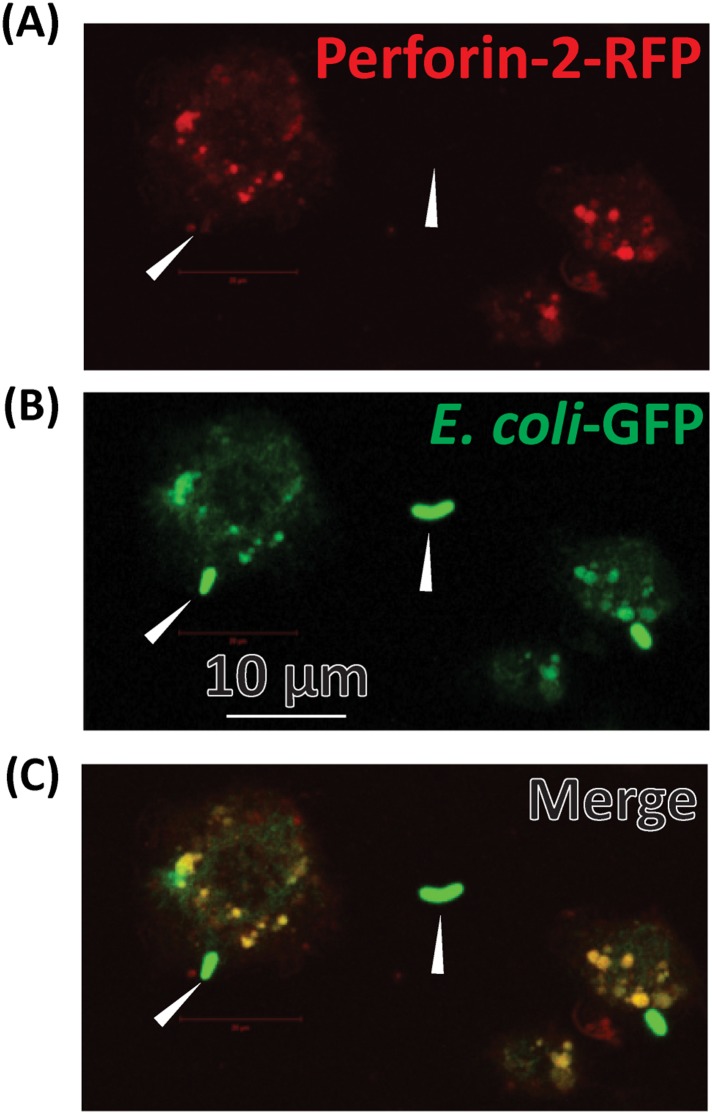
Figure 4. Endogenous Perforin-2 is located in intracellular sites allowing for rapid translocation to bacteria.
(A) Schematic demonstrating proposed orientation of Perforin-2 in vesicles. (B) Fractionation results of endogenous Perforin-2 from human macrophages. (Lane L) is a post-nuclear lysate control, (Lane 1–8) are individual fractions corresponding with specific indicated organelles. (C) Overexpression of murine Perforin-2-GFP in murine BV2 microglial cells. (D–F) Confocal images taken 5 min after S. typhimurium infection in Perforin-2-GFP + Perforin-2 siRNA transfected BV2 cells. White arrows denote extracellular S. typhimurium, red arrows highlight a DNA cloud corresponding with S. typhimurium (D) DAPI only, (E) Perforin-2-GFP only, (F) Merge of DAPI and Perforin-2-GFP. (G–I) Confocal images taken 5 min after Escherichia coli-GFP infection in Perforin-2-RFP + Perforin-2 siRNA transfected BV2 cells. Arrows point to extracellular E. coli-GFP that has made contact but is still extracellular with normal bacilli morphology maintained. (G) E. coli-GFP only, (H) Perforin-2-RFP only, and (I) merge E. coli-GFP and Perforin-2-RFP. Fractions in B were probed as follows: Cytoplasm—MEK1/2; Early Endosome—EEA1; Lysosome—Lamp1; ER—calreticulin; Golgi—Golgin-97; Mitochondria—Prohibitin; Peroxisome—Catalase; Plasma Membrane—Cadherin.