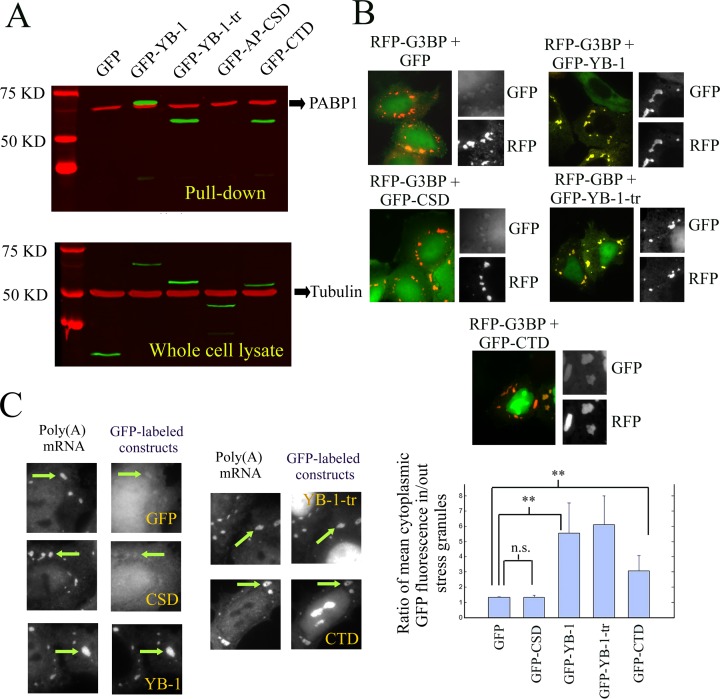
Figure 2.
Putative binding of YB-1, YB-1-tr, CTD and CSD to mRNA as tested by pull down assays or by detecting their presence in stress granules. (A) Western blot analysis of pull down assays from whole cell lysate of NRK cells expressing GFP-labeled YB-1 constructs. Oligo (T)25 magnetic beads were used to isolate Poly (A) mRNA and its protein partners. The GFP-labeled constructs were then detected using anti-GFP antibody (in green). Tubulin was used as a loading control for the whole cell lysates (anti-tubulin antibody in red). As revealed with anti-PABP1 antibody, the presence of PABP1 in the pull down fraction confirmed the effectiveness of the pull down assay to isolate Poly (A) mRNA. AP-CSD was the only YB-1 construct undetected in the pull-down fraction. (B) NRK cells were co-transfected with plasmids coding for one of the GFP-labeled YB-1 constructs and RFP-G3BP. The presence of the YB-1 constructs in G3BP-induced stress granules reveals their cellular affinity for mRNA. The presence of YB-1, YB-1-tr and CTD was clearly detected in stress granules (see arrows) in contrast with the CSD, which displays a similar distribution that GFP, used as control. Scale bar: 30 μm. Lower panel: Analysis of the relative enrichment of the various YB-1 constructs in stress granules. We measured the ratio of the relative increase of the mean intensity of GFP-labeled YB-1 constructs in stress granules compared to the surrounding cytoplasm. Such increase was significantly different compared to GFP for YB-1, YB-1-tr and CTD but not for CSD. Results are mean ± SD over 3 different samples, 10 cells per samples and 3 stress granules per cell. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; by t-test. (C) NRK cells were transfected with plasmids encoding for the indicated GFP-labeled YB-1 constructs and exposed to 0.3 mM arsenite for 45 min. In situ hybridization was then performed to reveal Poly (A) mRNA with Cy3-conjugated oligo(dT)40. Scale bar: 10 μm.