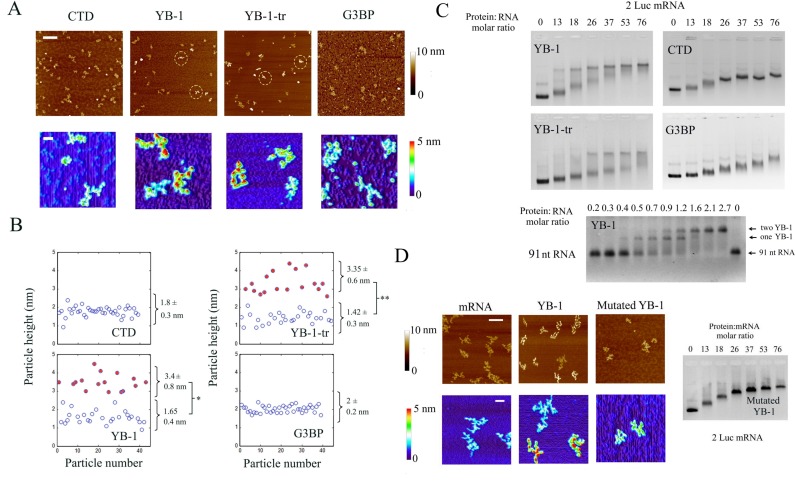
Figure 3.
YB-1 binds to mRNA in a cooperative manner via its cold-shock domain. (A) The formation of nucleoprotrein complexes in the presence of 2 Luc mRNA (2 nM) and the YB-1 constructs at concentration below saturation (50 nM) was analyzed by AFM on mica surface. Upper image: Large scale AFM images reveal an inhomogeneous binding of YB-1 and YB-1-tr to mRNA in contrast with CTD and G3BP used as control mRNA binding protein. Dashed circles indicate the presence of putative saturated mRNA:YB-1 complexes, which appear brighter than the other particles due to their height. Scale bar: 300 nm. Lower panel: The non-homogenous binding of YB-1 and YB-tr, which indicates a cooperative behavior, can be easily observed on higher magnification images. We also noticed the presence of the typical beads-on-a-string for the saturated complexes. Scale bar: 50 nm. (B) Analysis of the height distribution of the particles on mica. In contrast with CTD and G3BP, two significantly different populations can be extracted from the data obtained after the interaction of mRNA with YB-1 and YB-1-tr (see Figure S5). The population with larger (filled circles) and lower (empty circles) heights correspond to saturated YB-1:mRNA complexes and free or unsaturated mRNA, respectively (see Figure 1). Results are mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; by t-test. (C) Gel mobility shift assay reflecting the binding of CTD, YB-1, YB-1-tr and G3BP to 2 Luc mRNA and the binding of YB-1 to a short 91-bp RNA. At intermediary YB-1and YB-1-tr:2Luc mRNA molar ratios (from 13 to 37), the formed complexes split in two distinct bands in the gel corresponding to saturated YB-1:mRNA complexes and free or unsaturated mRNA, which indicates a cooperative binding of YB-1 to mRNA. Such cooperative binding is not apparent for CTD and G3BP as a progressive reduction of the nucleoprotein complex mobility is rather observed. For a short RNA (91 nt), we observe a step-by-step binding of YB-1, as shown by arrows. (See material and methods for experimental conditions of gel mobility shift assay). The binding of AP-CSD was not detected after gel mobility shift assays, which again indicates the low affinity of CSD for mRNA (Figure S8B). (D) Right panel: A gel mobility shift assay was performed to probe the binding of YB-1 to 2Luc mRNA after mutations of its cold-shock domain (Y72A and F74A). The binding of the YB-1 mutant appears to be non-cooperative. Left panel: The structure of 2 Luc mRNA (2 nM) in the presence or absence of wild-type or mutant YB-1 (50 nM) was analyzed by AFM on mica surface. In contrast with wild-type YB-1, we failed to observe the typical beads-on-a-string structure with the mutated YB-1. Scale bars: 150 and 50 nm for the highest and lowest magnifications, respectively.