Figure 6.
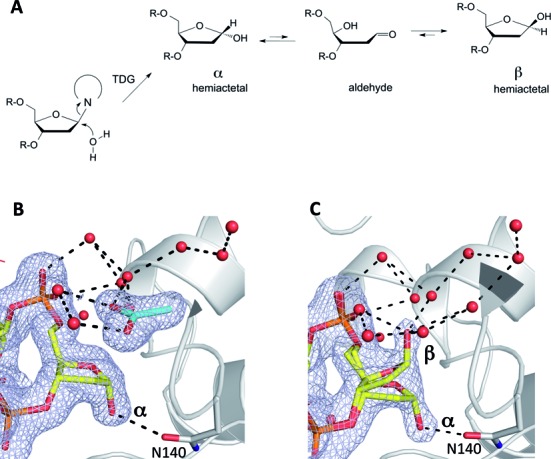
Anomeric structure of the abasic sugar observed in TDG enzyme-product complexes. (A) Abasic sites exist in several potential forms for enzyme-free DNA in solution. The α and β anomers of the cyclic hemiacetal predominate (together comprising 99%); minor forms are the ring-opened aldehyde and a hydrated aldehyde (not shown). For the TDG reaction, the initial enzyme-bound product resulting from C-N bond cleavage is expected to be the α anomer. (B) The α anomer is the predominant form of the abasic sugar observed for all TDGcat product complexes that include an acetate molecule in the active site (crystallized in the presence of 0.3 M acetate). (C) A roughly equal mix of α and β anomers is observed in a TDGcat product complex that lacks acetate in the active site. The β anomer appears to be stabilized by hydrogen bonds from C1’-OH to water molecules in the active site pocket.
