Figure 4.
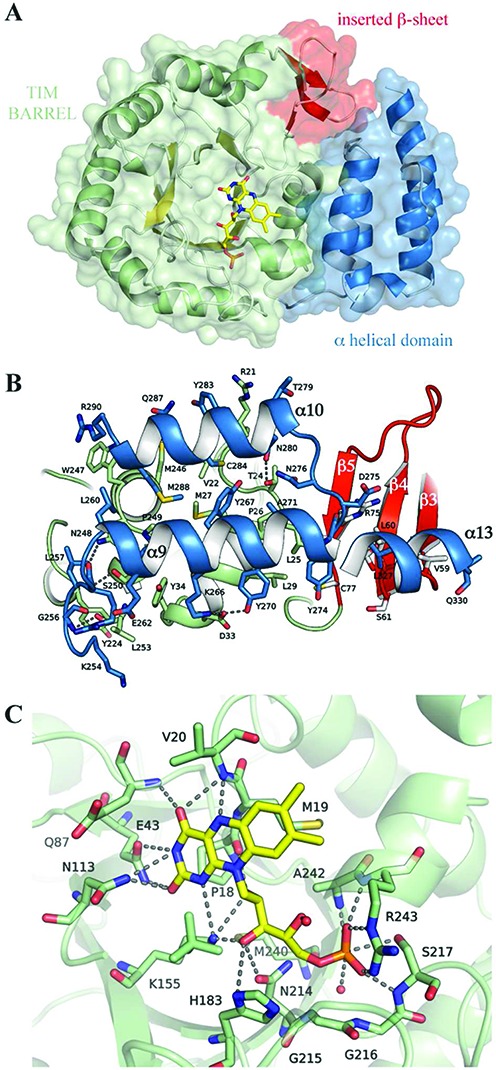
Structural characterization of the human Dus2 domain. (A) The structure of HsDus2dusD shows the typical (α/β)8 TIM barrel fold (α helices in green, β strands in yellow) but contains three additional β strands (red). The FMN coenzyme (yellow) lies at the center of the barrel. This domain is directly connected to the α-helical sub-domain (blue). (B) Molecular interface between the TIM barrel and the helical sub-domain. The interface is mainly hydrophobic and stabilized by hydrogen bonds, π−cation interactions (R21-Y283, R290-W247) and one salt-bridge (D33-K276). For clarity, residues belonging to α11, α12 and part of α13 are not displayed. (C) HsDus2 active site showing the molecular interaction between the FMN redox cofactor (yellow) and the residues in its immediate vicinity (green). For simplicity, only the major FMN conformation is displayed.
