Figure 1.
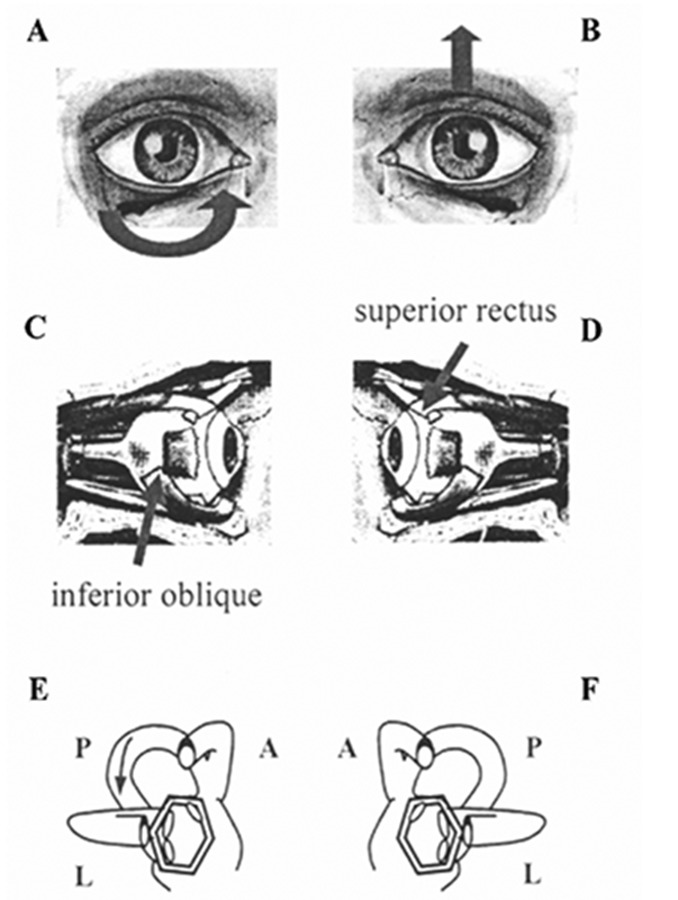
Paroxysmal positional nystagmus due to unilateral right posterior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (inhibitory stimulus). A and B) Arrows indicate the direction of nystagmus slow phase in the two eyes; C and D) arrows indicate the ocular muscles involved in nystagmus generation; E and F) the two labyrinths; arrow indicates the endolymphatic flow within the affected canal. A, C and E) The right eye and the right labyrinth; B, D and F) the left eye and the left labyrinth. A, anterior semicircular canal; L, lateral semicircular canal; P, posterior semicircular canal.
