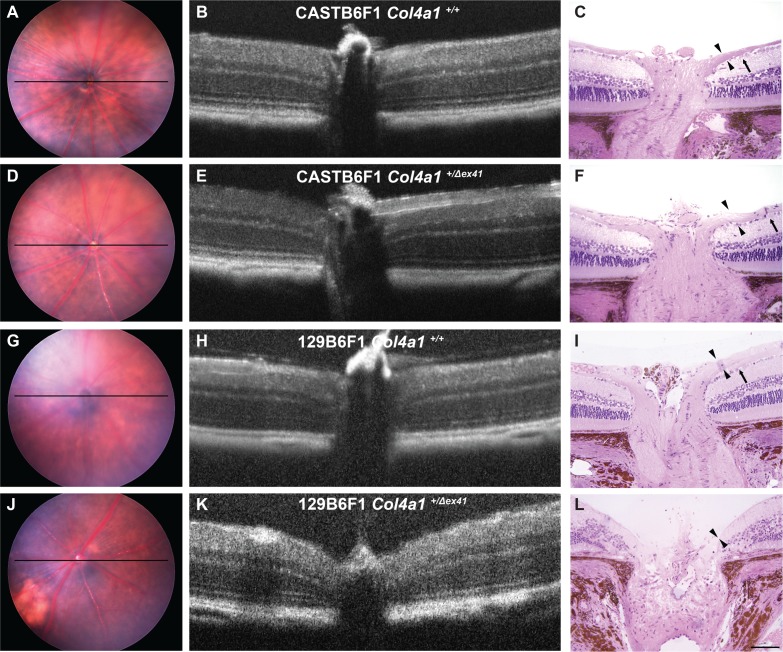
Figure 4.
Optic nerve head excavation in Col4a1+/Δex41 129B6F1 mice. Analyses of optic nerve heads from both Col4a1+/+ (A–C) and Col4a1+/Δex41 CASTB6F1 (D–F) revealed well-defined ganglion cells (arrow) and robust nerve fiber layers (arrowheads). In contrast, while control 129B6F1 eyes (G–I) had morphologically normal optic nerve heads in three of five Col4a1+/Δex41 129B6F1 eyes at 22 months (J–L), both the ganglion cell and nerve fiber layers were absent and the optic nerve head was cupped, a sign of severe glaucoma. Optical coherence tomography imaging is able to detect optic nerve cupping in vivo and, using OCT, we identified cupping in a portion of Col4a1+/Δex41 129B6F1 eyes. Among the 10 Col4a1+/Δex41 129B6F1 eyes independently examined by three investigators, six were unanimously considered as having optic nerve head cupping. In contrast, all Col4a1+/Δex41 CASTB6F1 eyes (n = 8) and eyes from Col4a1+/+ mice on either background (n = 8 and 6 for CASTB6F1 and 129B6F1, respectively) had normal optic nerve head morphology. Horizontal bars in fundus images (A, D, G, J) indicate the position of OCT scanning beams.