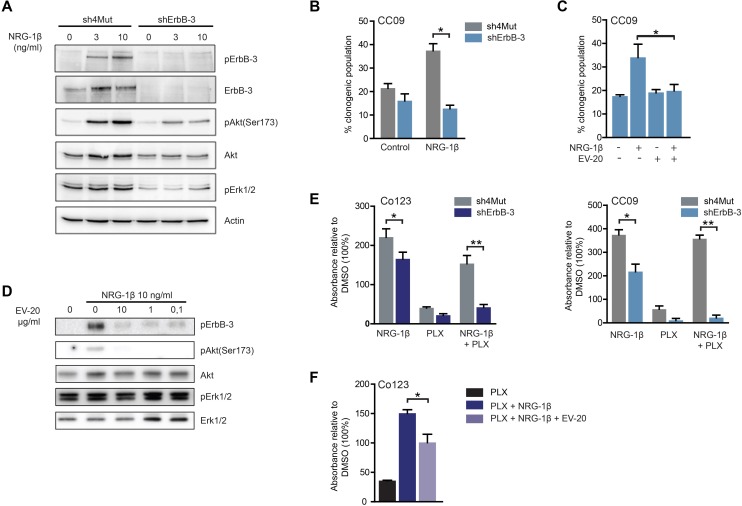
Figure 3. ErbB-3 is required for NRG-1β-dependent escape to Vemurafenib.
A. Immunoblot analysis of total and phosphorylated of ErbB-3 receptor and downstream signaling pathways evaluated in CC09 cells silenced for ErbB-3 (shErbB-3) as compared to same cells stably infected with the control vector (sh4Mut). After 24 hrs of growth factors deprivation, cells were stimulated with 10 ng/ml of NRG-1β for 5 minutes, then cell lysates were blotted as indicated. NRG-1β (10 ng/ml) stimulated clonogenicity was determined by limiting dilution assay in ErbB-3 silenced CC09 cells B. or in CC09 cells treated with 10 μg/ml of the anti-ErbB-3 antibody EV20 C. D. Co123 cells were cultured overnight in absence of growth factors and then treated with increasing doses of EV20 for 8 hrs before stimulation with NRG-1β (10 ng/ml) for 5 minutes; cell lysates were blotted as indicated. E. The rescue effect of NRG-1β (10 ng/ml) from Vemurafenib treatment (1 μM) was evaluated in CC09 and Co123 cells silenced for ErbB-3 (shErbB-3) as compared to control cells (sh4Mut). Proliferation was assessed by Cell Titer-Blue assay after 6 days of treatment either with NRG-1β (10 ng/ml) or Vemurafenib (1 μM) or a combination of the two. F. Proliferation, evaluated as in E, of BRAF mutant Co123 cells treated with Vemurafenib (1 μM) in the presence or absence of NRG-1β and EV20 (10 μg/ml). Results are expressed as mean +/− SD of two B. or three (C, E and F) independent experiments.* = p < 0.05, ** = p <0.01 (t-test).