Figure 6. Schematic representation summarizing the proposed role of melatonin in cancer stem cells.
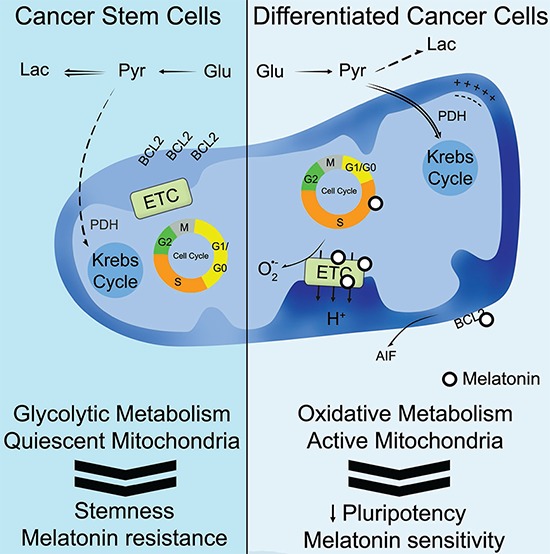
Our hypothesis ascribes an anti-tumor effect for melatonin only in differentiated cancer cells with an active oxidative metabolism, triggering a type of mitochondrial-mediated cell death which is likely to be characterized by an arrest at S-phase, reduction of the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC), generation of reactive oxygen species, BCL-2 down-regulation and AIF releaseThus, the treatment with melatonin and the stimulation of mitochondrial metabolism constitute promising strategies against resistant cancer stem cells.
