Figure 1. RBP2 expression was positively correlated with differentiation status and distant metastasis in primary gastric cancer tissues and it is involved in GC progression and GC stemness property maintenance.
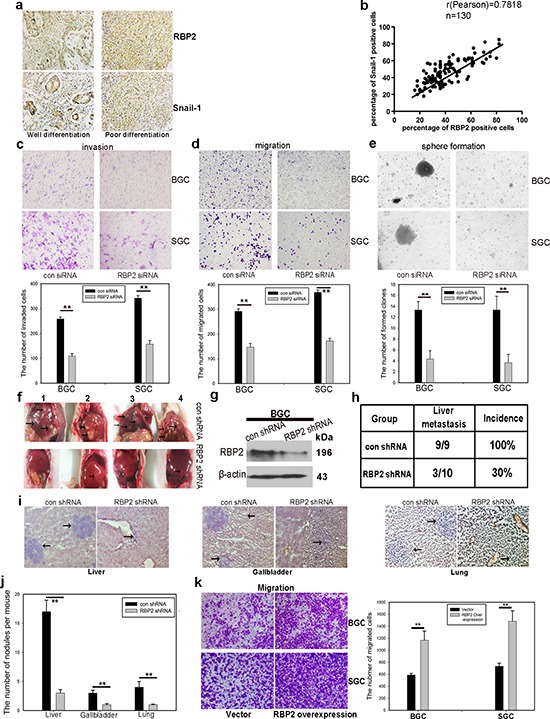
a. Representative images of RBP2 and Snail-1 expression in differentiation status. b. RBP2 and Snail-1 expression was positively correlated in clinical specimen. c and d. Knockdown of RBP2 decreases cell invasion (c) and cell migration (d) Data are mean ± SD of 3 biological replicates, **p < 0.01 compared with negative control. Original magnification, × 40. e. Stem cell property is jeopardized with RBP2 inhibition. Data are mean±SD of 3 biological replicates, **p < 0.01 compared with negative control. Original magnification, × 40. f. RBP2 suppression significantly decreases liver metastasis. Black arrows indicate the metastatic tumor nodules. g. western blot indicates the inhibition of RBP2 in lenti-virus mediated stable-transfection BGC-823 cells. h. Decrease of liver metastasis incidence in RBP2 shRNA group. i. and j. HE staining of liver, gallbladder and lung, which shows decrease of metastatic tumor nodules formed in RBP2 shRNA group. Representative images are shown here. Black arrows indicate the metastatic tumor nodules. Original magnification, × 40. Data are mean ± SD of 3 biological replicates, **p < 0.01 compared with negative control. k. RBP2 overexpression enhanced migration of gastric cancer cells. Original magnification, × 40. Data are mean ± SD of 3 biological replicates, **p < 0.01 compared with negative control.
