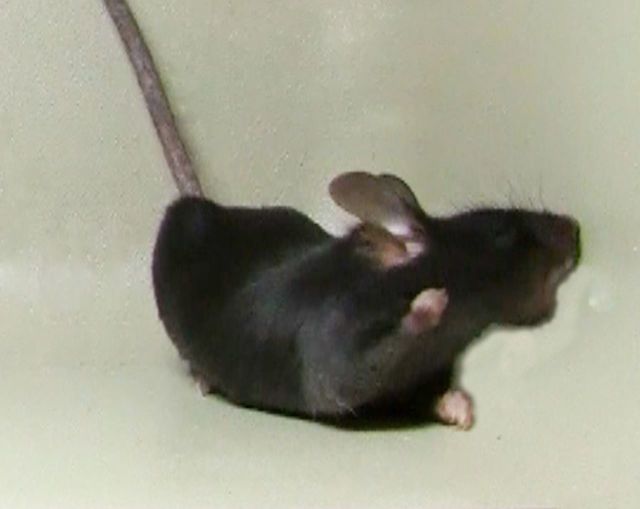
To better understand the dopaminergic defects that give rise to dystonia, Rose et al. generate a knockin mouse model of L-DOPA-responsive dystonia that recapitulates the core features of the human disorder. The timing and extent of dopamine deficiency in combination with abnormal D1 and D2 receptor responses mediates dystonia development.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.