Figure 6.
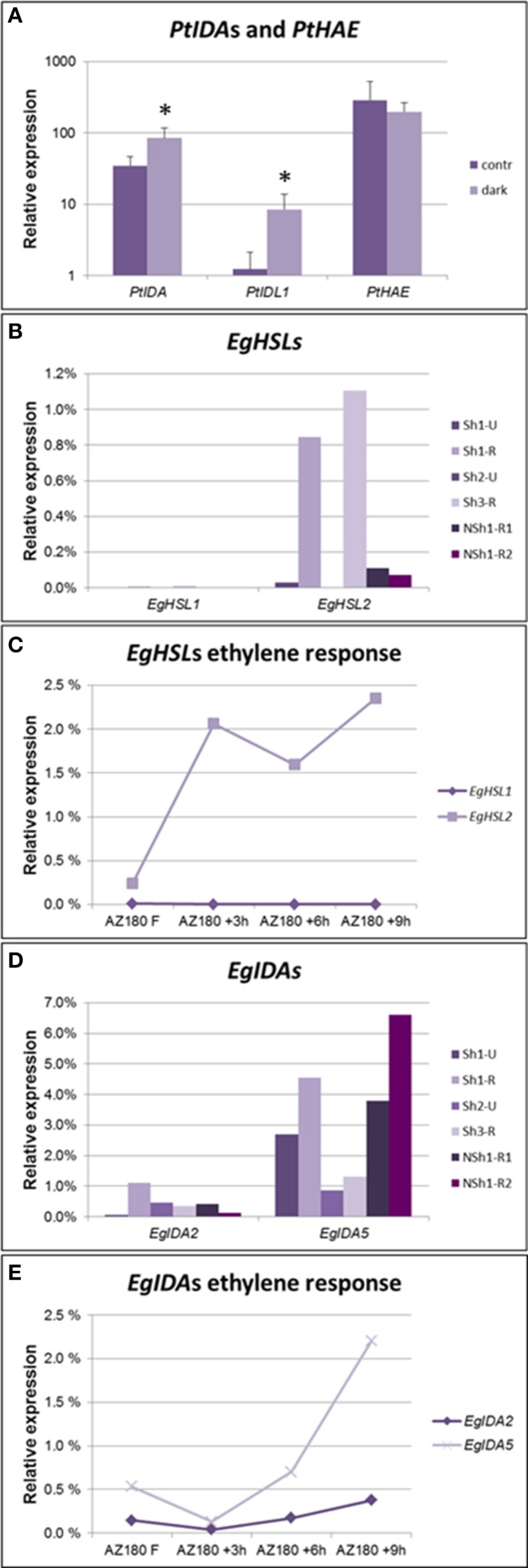
Expression levels of genes encoding IDA ligands and HSL receptors in AZs. (A) qPCR detecting increased expression levels of Populus IDA genes, but not the PtHAE gene in axils of shade-treated leaves prone to abscise compared to axils in non-shaded, non-abscission aspen leaves. qPCR, averages and standard deviations of three biological replicates. Normalized to PtACTIN1 expression. *p < 0.05, t-test, non-shaded vs. shaded. (B) qPCR analysis of oil palm EgHSL1 and EgHSL2 expression in AZs from unripe (Sh1-U and Sh2-U) not actively abscising fruit and AZs of ripe (Sh1-R, Sh3-R) actively abscising fruit, as well as AZs from ripe fruit of a non-abscising tree (NSh1-R1, NSh1-R2). (C) qPCR analyses of oil palm EgHSL expression during ethylene-induced abscission in ripe 180 DAP fruits. Samples were taken after 0, 3, 6, and 9 h treatment with ethylene. Similar results were obtained when treating 145 DAP fruits (Supplementary Figure S3C). In both experiments fruit separated by 9 h of ethylene treatment. (D) qPCR analysis of oil palm EgIDA2 and EgIDA5 expression in the AZs of unripe (Sh1-U and Sh2-U) not actively abscising fruit and AZs of ripe (Sh1-R, Sh3-R) actively abscising fruit, as well as AZs from ripe fruit of a non-abscising tree (NSh1-R1, NSh1-R2). Expression levels of additional EgIDA genes are found in Supplementary Figure S3D. (E) qPCR analyses of oil palm EgIDA2 and EgIDA5 expression during ethylene-induced abscission in ripe 180 DAP fruits. Samples were taken after 0, 3, 6, and 9 h treatment with ethylene. Similar results were obtained when treating 145 DAP fruits (Supplementary Figure S3E). In both experiments fruit separated by 9 h of ethylene treatment.