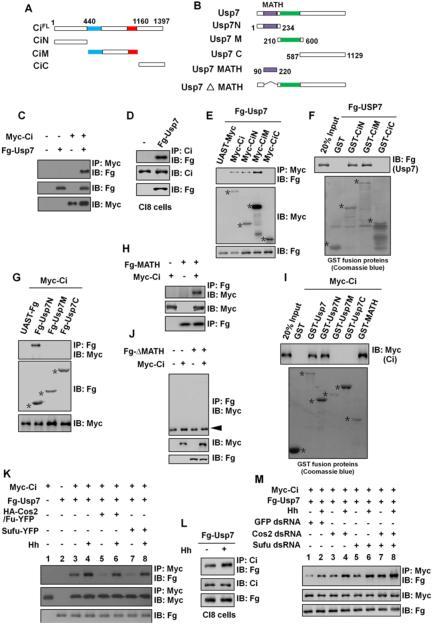
Figure 2. Usp7 binds Ci through Its MATH Domain.
(A and B) Schematic drawings show the domains or motifs in Ci and Usp7 and their truncated fragments used in subsequent Co-IP and pull-down assays. Blue and red bars denote the Zn finger DNA binding and dCBP binding domains of Ci. Purple and green bars represent MATH domain and core catalytic domain of Usp7.
(C) Fg-Usp7 interacted with Myc-Ci in S2 cells.
(D) Fg-Usp7 interacted with endogenous Ci in Clone8 cells.
(E) Fg-Usp7 associated with Myc-tagged N- and M-fragments of Ci. Asterisks indicate expressed Ci deletion mutants.
(F) Extracts from S2 cells expressing Fg-Usp7 were incubated with GST or indicated GST fusion proteins. The bound proteins were analyzed by western blot. Asterisks mark GST fusion proteins.
(G) Usp7 interacted with Ci through its N-region in S2 cells. Asterisks mark expressed Usp7 truncated fragments.
(H) Fg-Usp7-MATH associated with Myc-Ci in S2 cells.
(I) GST pull-down between Myc-tagged Ci and GST or GST-tagged Usp7 fragments. Asterisks indicate expressed GST fusion proteins.
(J) MATH domain-deleted form of Usp7 did not bind Ci in S2 cells. The arrowhead indicates IgG.
(K) Cos2-Fu and Sufu competed Usp7 to bind Ci with or without Hh-conditioned medium treatment. S2 cells were treated with MG132 for 4hrs prior to harvesting the cells.
(L) Hh-conditioned medium treatment promoted endogenous Ci binding to Fg-Usp7 in Clone8 cells.
(M) Knockdown of cos2 or/and sufu promoted Ci binding to Usp7 in absence or in presence of Hh-conditioned medium treatment. S2 cells were treated with MG132 for 4hrs prior to harvesting the cells.
See also Figure S2 and S3.