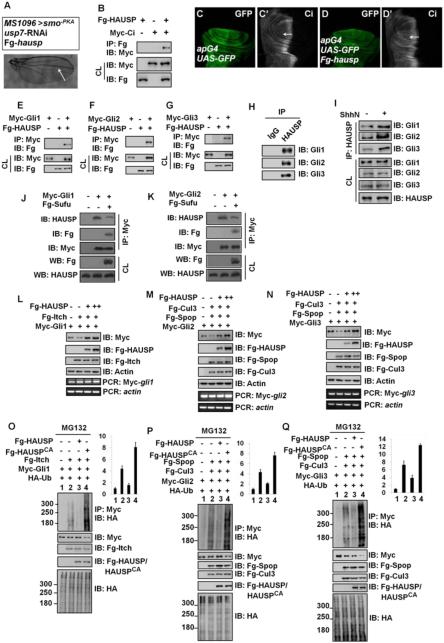
Figure 6. HAUSP Binds and Deubiquitinates Gli Proteins.
(A) Adult wing that expressing usp7 RNAi and Fg-tagged hausp. Arrow marked the space between vein3 and vein4.
(B) Fg-HAUSP could bind Myc-Ci in S2 cells.
(C-C’) A wing disc of apG4 was stained to show GFP (green) and Ci (white).
(D-D’) Overexpression of hausp by apG4 resulted in an increase of Ci (white, arrow) in wing discs.
(E-G) Fg-HAUSP could bind Myc-Gli1, Myc-Gli2 and Myc-Gli3 in 293T cells, respectively. The expression of corresponding proteins from cell lysis (CL) was shown below.
(H) Endogenous HAUSP pulled down endogenous Gli1, Gli2 and Gli3 in 293T cells. The cells from one 10cm plate were lysed and the lysis was equivalently divided two parts for IP with control IgG or HAUSP antibody.
(I) ShhN treatment increased the interaction between endogenous HAUSP and endogenous Gli proteins in 293T cells.
(J-K) Sufu expression inhibited the interaction between HAUSP and Myc-tagged Gli1 (J) and Gli2 (K) in Sufu−/− MEF cells. The transfected cells were treated with MG132 for 4hrs prior to cell harvesting.
(L-N) HAUSP blocked Gli protein degradation mediated by corresponding E3 ligases. 293T cells were transfected with indicated plasmids. Actin is shown as a loading control. RT-PCR analysis was performed to test the levels of Myc-gli mRNA. The forward primer was on Myc tag, whereas the reverse primer was on gli. actin acts as a control. (O-Q) HAUSP inhibited, but HAUSPCA promoted the ubiquitination of Gli proteins mediated by according E3 ligases. 293T were transfected with indicated plasmids and treated with MG132 for 4hrs before cell harvesting. Quantification analyses of the ubiquitination levels of Gli proteins were shown on right. The results were presented as means±SD of values from three independent experiments.
See also Figure S5.