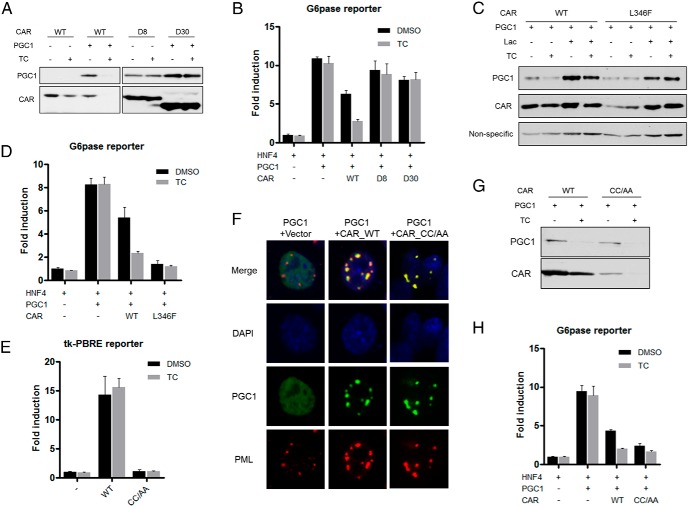
Figure 6.
CAR-mediated inhibition of PGC1α requires active AF2 domain but is independent of DNA-binding. A, Cotransfection of PGC1α and WT CAR or D8 and D30 in 293T cells with or without TC (500nM) treatment for 24 hours, followed by immunoblotting to detect the protein level of PGC1α and CAR. B, The suppressive effect of CAR D8 and D30 on PGC1α activity was measured by G6Pase luciferase reporter assay. C, Cotransfection of PGC1α and WT CAR or L346F mutant in 293T cells with or without TC treatment (500nM, 24 h), followed by immunoblotting to detect the protein level of PGC1α and CAR. “Nonspecific” denotes the nonspecific band detected by the PGC1 antibody, which was used as a loading control. D, The suppressive effect of CAR L346F mutant on PGC1α activity was measured by G6Pase luciferase reporter assay. E, The transcriptional activity of WT CAR or CC/AA was measured by using the tk-PBRE reporter assay. PBRE, phenobarbital-response element. F, HepG2 cells were cotransfected with PGC1α, WT CAR or CC/AA, followed by immunofluorescent detection of PGC1α, CAR, and the endogenous PML. G, Cotransfection of PGC1α and WT CAR or CC/AA in 293T cells with or without TC treatment, followed by immunoblotting to detect PGC1α and CAR. H, The suppressive effect of WT CAR or CC/AA on PGC1α activity was measured by G6Pase luciferase reporter assay.