Figure 7.
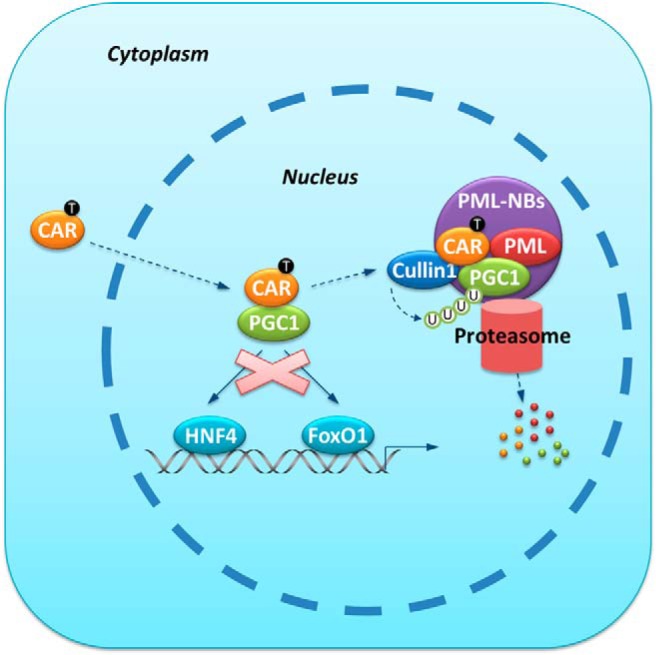
Mechanism of CAR-mediated suppression of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Hepatic gluconeogenic gene expression is facilitated by PGC1α-mediated coactivation of transcription factors such as HNF4 and FoxO1 during fasting or under the diabetic condition. When bound by its ligand TCPOBOP, CAR enters the nucleus and physically interacts with PGC1α. The CAR-PGC1α interaction results in the targeting of both proteins to the PML-NBs, where CAR-associated Cullin1 E3 ligase modifies PGC1α with poly-ubiquitin chain and promotes the proteasomal degradation of PGC1α. The gluconeogenic gene expression is inhibited due to the compromised availability of the PGC1α protein.
