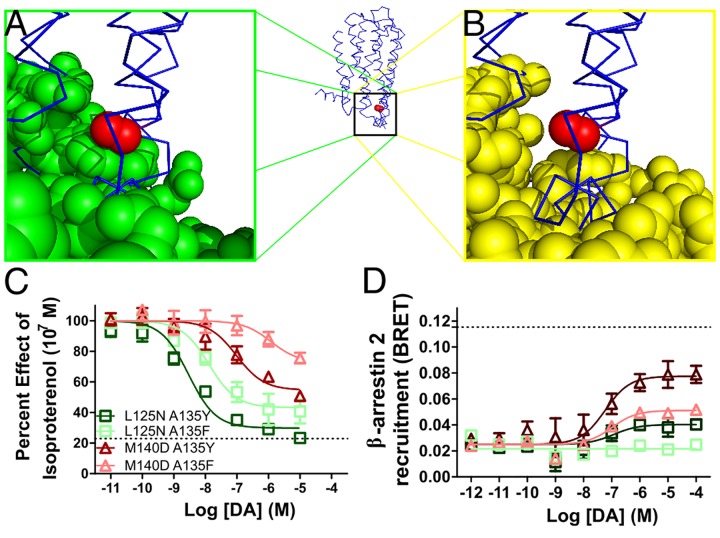
Fig 2. Receptor control of partial agonism at D2R with A135 mutations.
(A) Relative proximity of G proteins (green spheres) and A135 (red sphere) in D3 (blue ribbon, PDB ID: 3PBL [37]) as determined by alignment of D3R to β2AR in receptor/G protein complex (PDB ID: 3SN6, [38]). (B) Arrestin (yellow spheres) does not reside close to A135 when D3R is aligned to rhodopsin in receptor/arrestin complex (PDB ID: 4ZWJ [39]). (C) G protein activity as determined by inhibition of isoproterenol-induced cAMP accumulation is titrated by substitution of A135 with a bulky polar (tyrosine) or nonpolar (phenylalanine) residue and combined with L125N or M140D to impart controlled loss of G protein function. (C) β-arrestin 2 recruitment as determined by BRET is similarly controlled. All data are presented with SEM from n = 3–5 independent experiments, with statistical significance calculated in S1 Table.