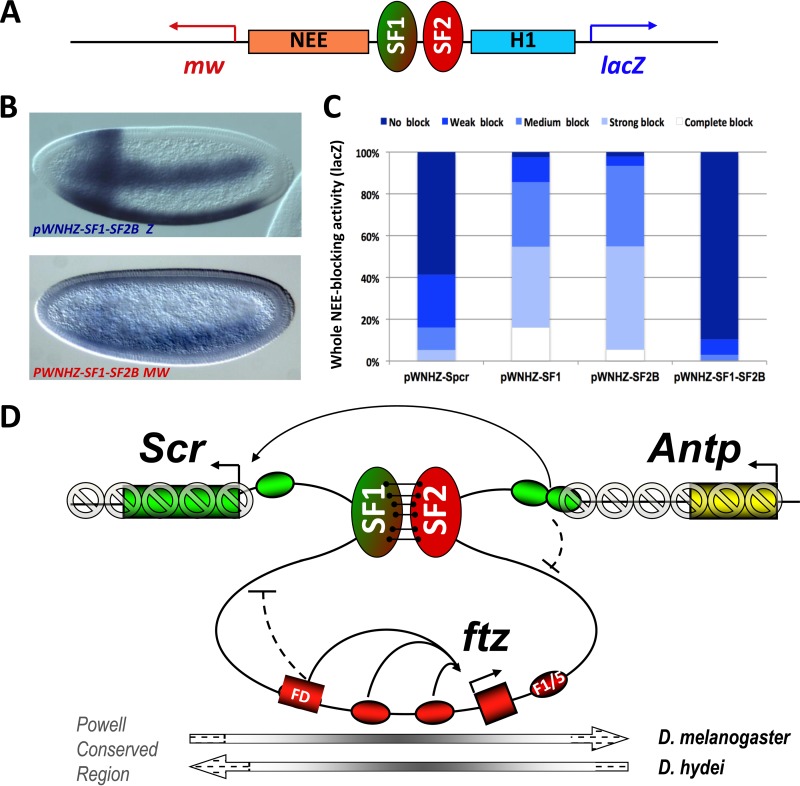
FIG 7.
The SF1-SF2 loop remodels enhancer traffic and modulates chromatin structure in the Scr-Antp region. (A) Diagram of the enhancer bypass transgene containing tandemly paired SF1 and SF2B insulators between NEE and H1 in the pWNHZ vector (see Fig. 6A and Materials and Methods). (B) Representative images of transgenic embryos containing the bypass transgene after hybridization with anti-lacZ (top) or antiwhite (bottom) RNA probes. (C) Quantitation of NEE blocking in pWNHZ-SF1SF2B bypass transgenic embryos stained with the lacZ probe. Quantitation of spacer and single insulator controls are from Fig. 6K. (D) Model showing SF1 attached to SF2, leading to the formation of a chromatin loop that contains the entire the ftz transcription unit. The loop may restrict access between enhancers and promoters of neighboring genes (blocked arrows). It may allow the Scr distal enhancers and PRE element to bypass the SF1 block (long curved arrow). The loop may also insulate the ftz domain from the encroachment of repressive chromatin assembled on Scr and Antp genes in the anterior tissues (shaded block signs). Arrows below the map show the evolutionarily conserved Powell genomic region (see Discussion).