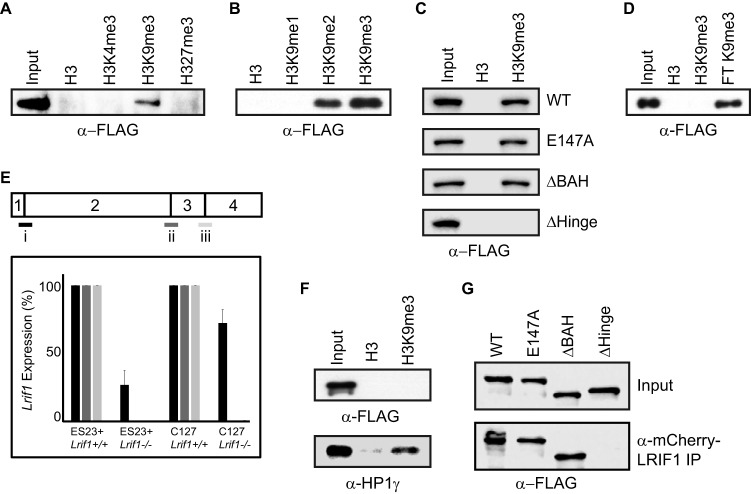
FIG 6.
LRIF1 mediates indirect interaction of SMCHD1 with H3K9me3-modified chromatin. (A to D) Western blots of bound proteins following peptide pulldown experiments on nuclear extracts from ES23+ ESCs with unmodified H3, H3K4me3, H3K9me1/2/3, and H3K27me3 peptides (A and B) and on nuclear extracts from ES23 ESCs complemented with WT or mutant SMCHD1-FLAG derivatives and H3K9me3 peptide (C) and full-length recombinant SMCHD1 (rSMCHD1) and H3K9me3 peptide (D). The flowthrough (FT) lane shows that rSMCHD1 remains in solution and is not bound to the H3K9me3 peptide. (E) Quantitative RT-PCR to verify the loss of transcript in Lrif1−/− cell lines created by CRISPR mutagenesis of exon 3/4. A schematic of the Lrif1 coding sequence is drawn with numbered exons, with three primer sets spanning intron/exon boundaries for qRT-PCR below (i to iii). Lrif1 expression in the mutant clones is shown as a percentage relative to the expression level in the wild-type parental cell line. Both the ES23+ and C127 Lrif1−/− cell lines show reduced transcript levels with primer set i and a loss of transcript with primer sets ii and iii. (F) Western blots for SMCHD1-FLAG and HP1γ (control) following peptide pulldown experiments with nuclear extracts from Lrif1−/− ES23+ ESCs. (G) Anti-FLAG Western blotting with mCherry-LRIF1 immunoprecipitation of nuclear extracts from HEK293T cells cotransfected with mCherry-LRIF1 and SMCHD1-FLAG derivatives. Input, 10%; IP, 30%.