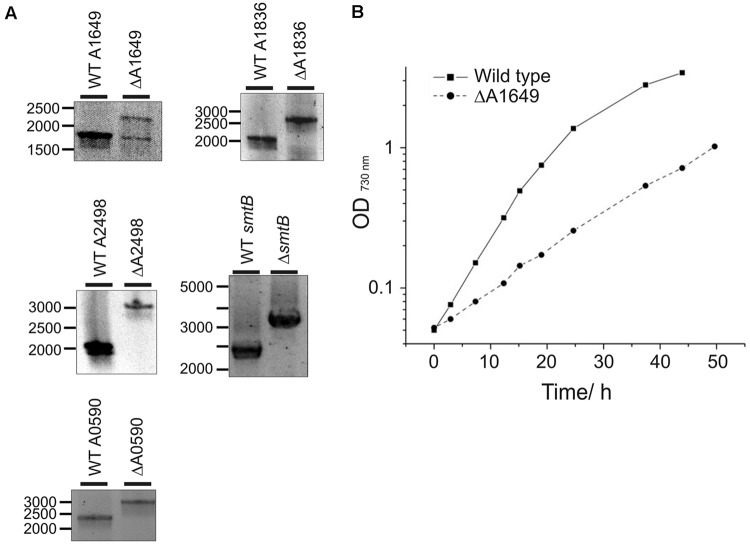
FIGURE 1.
Segregation analysis of deletion mutants and growth of the merodiploid SYNPCC7002_A1649 strain. (A) Electrophoretic analysis of PCR amplicons produced using DNA templates derived from the wild-type (WT) strain and SYNPCC7002_A1649 (ΔA1649), SYNPCC7002_A1836 (ΔA1836), SYNPCC7002_A2498 (ΔA2498), SYNPCC7002_A2564 (ΔsmtB), and SYNPCC7002_A0590 (ΔA0590) mutant strains of Synechococcus 7002. For the SYNPCC7002_A1649 (fur) mutant, the expected amplicon size was 1.82 kb for WT and 2.35 kb for the mutant, respectively. Note that the mutant is a stable merodiploid with approximately equal copies of each allele (fur and fur::aadA). For SYNPCC7002_A1836 (perR), the expected amplicon size was 2.12 kb for WT and 2.72 kb for the mutant. For SYNPCC7002_A2498 (zur), the expected amplicon size was 1.99 kb for WT and 3.11 kb for the deletion mutant, respectively. The amplicon sizes for smtB were 2.33 kb (WT) and 3.14 kb (mutant), and for SYNPCC7002_A0590 amplicons had 2.29 kb (WT) and 3.02 kb (mutant), respectively. (B) Growth of Synechococcus 7002 WT and the merodiploid SYNPCC7002_A1649 (fur)::aadA strain in A+ medium. The growth medium for the latter strain contained 50 μg/mL spectinomycin for continuous selection. The cultures were grown under standard growth conditions, and representative growth curves for these two strains are displayed. Growth of the other mutant strains investigated in this study was wild type-like.