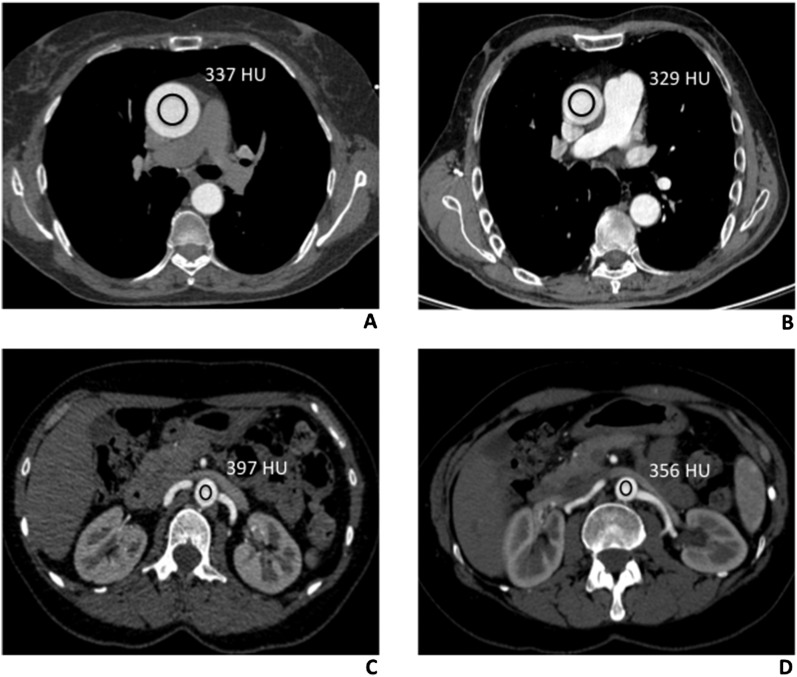
Figure 2.
Density measurements (Hounsfield units) of thoracic and abdominal aorta in low and standard tube voltage CT angiography (CTA) studies. (a) 100 kV protocol CT scan of a 57-year-old male, with no aortic disease. Axial CTA thoracic image showing a region of interest (ROI) in the lumen of the ascending aorta, at the level of the common pulmonary artery (337 HU). (b) Comparative image of a 62-year-old male, with no aortic disease, evaluated with the 120 kV protocol. Axial CTA thoracic image, acquired at the same level, showing the ROI in the ascending aortic lumen, with the corresponding value of 329 HU. (c) A 68-year-old male, who had undergone CTA study with the 100 kV protocol. Axial CT abdominal scan, with the rounded ROI drawn into the abdominal aortic lumen (397 HU), at the origin of renal arteries. (d) Comparative image of a 65-year-old male, evaluated with the 120 kV protocol. Axial CTA scan, with the ROI drawn into the lumen of the abdominal aorta (356 HU), at the same level.