Figure 1. Workflow for Investigating the Urine Proteome.
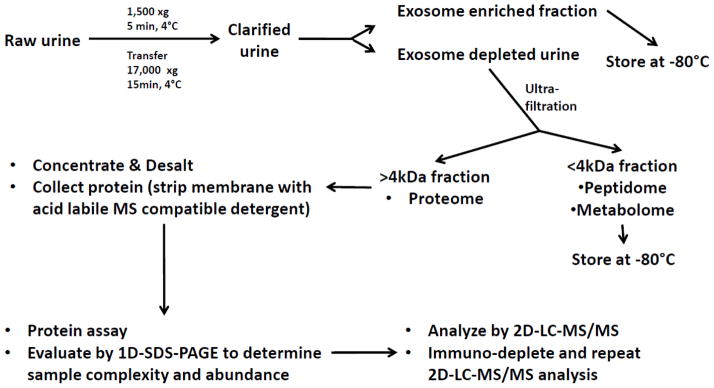
Urine is initially clarified of cells and debris by routine centrifugation. The acquired cellular sediments are stored for future studies. The clarified urine is then subjected to ultracentrifugation across sucrose density gradients to isolate exosomes and microparticles. The exosome and microparticle-depleted urine is then processed using size fractionating filters that partition the urine into fractions containing proteins and peptides either less than or greater than 4 kDa. The low molecular weight fraction is then stored for peptidomic and metabolomics studies. If proceeding to proteomic analysis the proteins >4kDa are stripped from the ultrafiltration membrane and the analyte is concentrated and de-salted before analysis by mass spectrometry. Immunodepletion can be used to remove the most highly abundant proteins from urine and improve resolution for low-abundance proteins.
