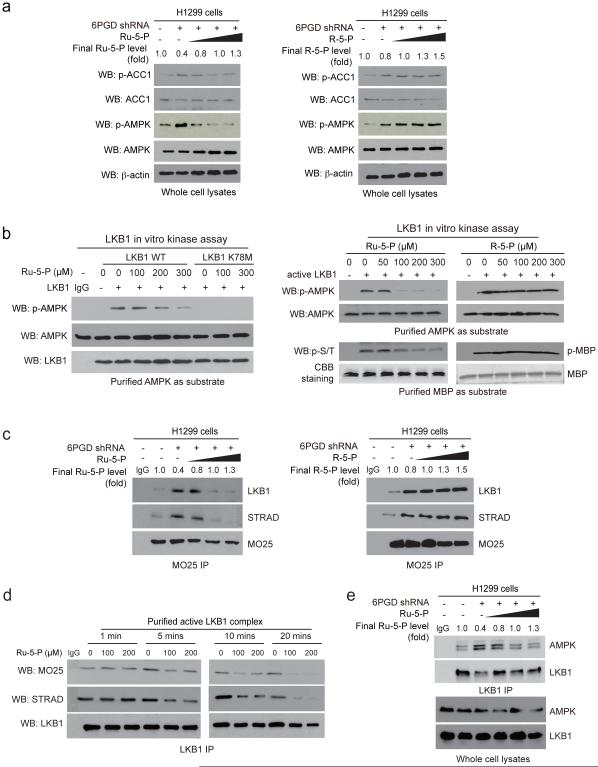
Fig. 4.
Ru-5-P inhibits LKB-AMPK pathway by disrupting active LKB1 complex. (a) Cell lysates from 6PGD KD H1299 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of Ru-5-P (left) or R-5-P (right) for 4 hours, followed by Western blot for phosphorylation levels of AMPK (pT172) and ACC1 (pS79). Final levels (fold) of Ru-5-P or R-5-P were normalized to the control vector cells without treatment. (b) In vitro LKB1 kinase assays were performed using LKB1 wild type (WT) or a kinase dead form (K78M) purified from A549 cells (left panel) or LKB1 WT purified from H1299 cells (right panel) incubated with recombinant AMPK (left and upper right) or MBP (lower right) as substrates in the presence of increasing concentrations of Ru-5-P (left), or Ru-5-P or R-5-P (right) at 37 °C for 20 minutes. Samples were applied for Western blot. (c) Cell lysates of 6PGD KD H1299 cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of Ru-5-P (left) or R-5-P (right), followed by immunoprecipitation of MO25 and Western blot to detect co-immunoprecipiated LKB1 and STRAD. (d) Purified active LKB1 complex purchased from Upstate (Millipore) were incubated with Ru-5-P (100 or 200 μM) for indicated time points, followed by immunoprecipitation of LKB1 and Western blot to detect co-immunoprecipiated MO25. (e) Cell lysates of 6PGD KD H1299 cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of Ru-5-P, followed by immunoprecipitation of LKB1 and Western blot to detect co-immunoprecipiated AMPK. (a-e) Results of one representative experiment from at 2 independent experiments (a-b) and 3 independent experiments (c-e) are shown. Uncropped Western blots are provided in supplementary Figure 9.