Figure 3. Therapeutic Strategies to Ameliorate Amyloidosis.
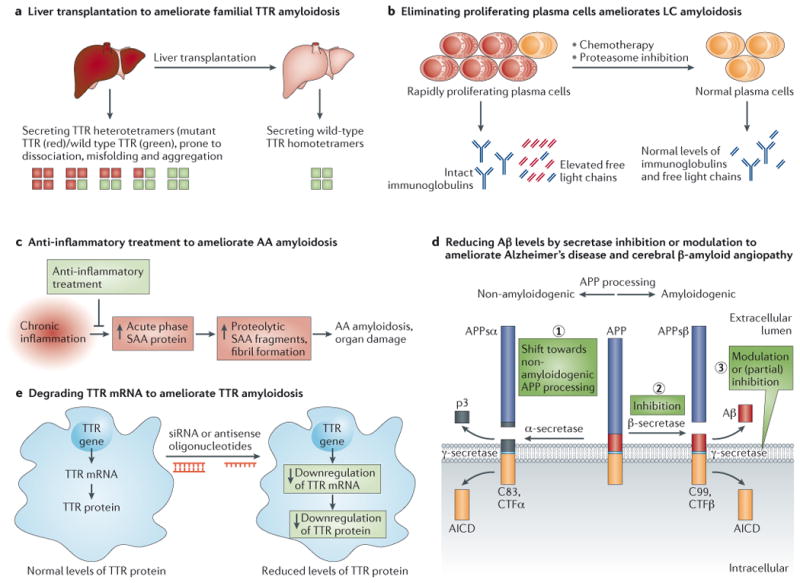
A. Gene therapy by liver transplantation to treat Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy (FAP). Since TTR is largely produced by the liver, liver transplantation was introduced in the 1990s as a therapy for early stage patients with FAP. Wild type (WT) TTR tetramers (depicted with green squares) produced by the donor liver are much less amyloidogenic than the mutant TTR/WT TTR heterodimers (depicted with red and green squares, respectively) produced by the patient's liver before transplant. This approach successfully slows the progression of FAP and extends life span, but requires organ availability, life-long immunosuppression, and is associated with 10% mortality due to the transplant procedure.
B. Protein reduction by chemotherapy to treat Light Chain Amyloidosis (AL). The amyloidogenic protein in AL amyloidosis is an immunoglobulin light chain or a fragment thereof overproduced by a plasma cell dyscrasia. Removal of the proliferating cancerous plasma cells producing the amyloidogenic light chain by chemotherapy regimens, with or without autologous stem cell transplantation, is used for patients without major cardiac involvement that are not too sick to tolerate these aggressive regimens, which leads to apparently durable disease remission.
C. Anti-inflammatory treatment dramatically lowers acute phase serum amyloid A (SAA) protein production for the treatment of Amyloid A Amyloidosis (AA amyloidosis). Systemic amyloid A amyloidosis is a long-term complication in some patients suffering from chronic infection or chronic inflammation (e.g., chronic inflammatory arthritis). The amyloidogenic protein is derived by proteolysis of SAA, an acute-phase reactant protein transcriptionally upregulated during inflammation. Persistent high concentrations of SAA fragments in plasma above a critical threshold for aggregation can trigger AA deposition. Treatment of the underlying infectious or inflammatory trigger can reverse this type of amyloidosis, if diagnosed early.
D. Reduction of pathogenic Aβ levels by secretase inhibition or modulation has therapeutic potential for Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Cerebral β-Amyloid Angiopathy. The amyloid precursor protein (APP) is a transmembrane protein that is constitutively cleaved by enzymes called secretases. Endoproteolytic processing via the non-amyloidogenic pathway, i.e., α-secretase cleavage followed by γ-secretase cleavage (shown on left) generates non-amyloidogenic APP fragments. In contrast, processing by β-secretase and subsequent γ-secretase cleavage produces amyloidogenic Aβ peptides (shown in red on right). Aggregation of Aβ peptides into extracellular amyloid fibrils or plaques is a histopathological hallmark and a diagnostic criterion for Alzheimer's disease. Reduction of Aβ peptide concentration can be achieved by (1) shifting APP processing towards non-amyloidogenic endoproteolysis, or (2) inhibition of β-secretase , or (3) γ-secretase inhibition or modulation. Inhibition of γ-secretase was shown to be feasible experimentally, however, side effects are a concern due to its many substrates. Interestingly, γ-secretase cleavage generates Aβ peptides of various lengths—as a rule of thumb, the longer the peptide, the more amyloidogenic. Modulation of γ-secretase processing of APP to generate shorter, less amyloidogenic Aβ peptides is currently being investigated.
E. Gene silencing by siRNA or antisense oligonucleotides for the treatment of Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy (FAP). Recently published early-stage, small, placebo-controlled clinical trial data has identified small interfering RNAs (siRNA, also RNAi) that lower mutant and WT transthyretin (TTR) protein production in patients with FAP. Analogous clinical data on antisense oligonucleotides that degrade TTR mRNA and thus lower TTR production and secretion into the blood from the liver are promising.
