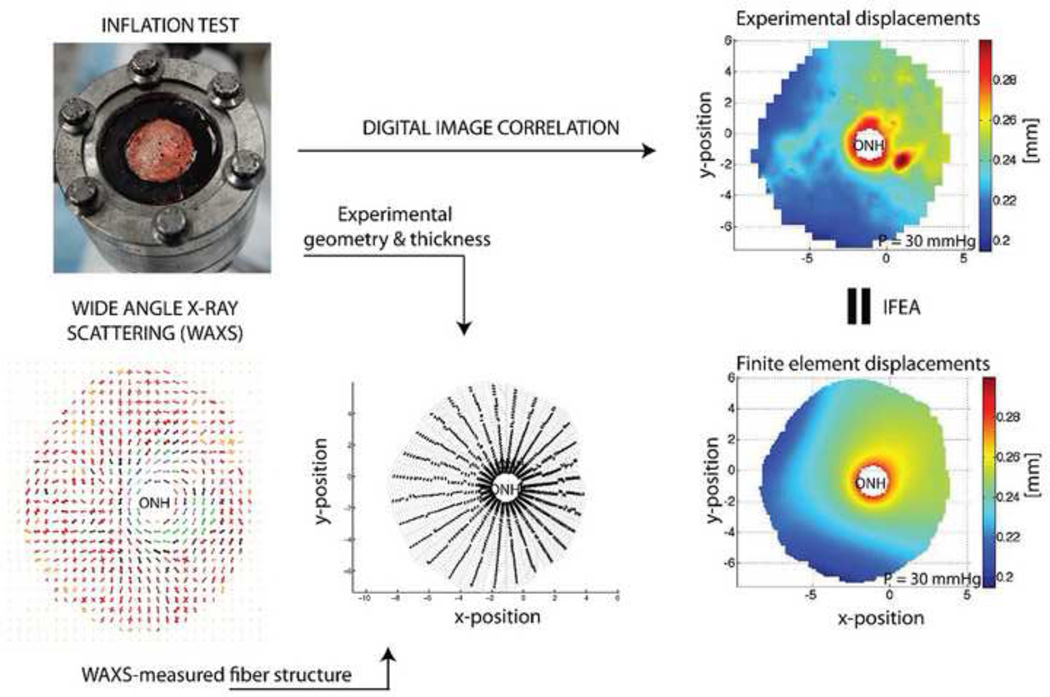
Figure 6.
Overview of ocular inflation testing and inverse finite element analysis (IFEA). An eye or posterior segment is clamped in a chamber (top left) and pressurized while measuring scleral deformation (top right). The scleral shell geometry and thickness are measured (bottom middle) and combined with information about collagen fiber orientation (bottom left) in a finite element model that predicts scleral displacements (bottom right). Iterative adjustment of tissue mechanical properties in the finite element model until approximate matching of measured and computed displacements allows deduction of local tissue mechanical properties. Top left panel reproduced from (Coudrillier et al., 2012).