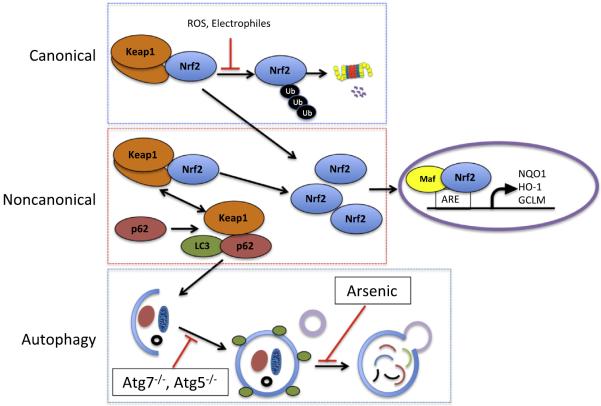
Fig. 1.
The canonical and noncanonical regulatory pathways of Nrf2 signaling. (1) Canonical pathway: under normal conditions, Nrf2 is bound to the E3 ubiquitin ligase adaptor protein Keap1, which leads to its ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation. When Keap1 is challenged with ROS or electrophiles, critical cysteines are modified, blocking Nrf2 ubiquitylation, increasing the level of Nrf2 and activating the ARE-mediated transcription. (2) Noncanonical pathway: when autophagic flux is compromised and p62 accumulates, Keap1 is sequestered by p62 and can no longer bind Nrf2, leading to increased Nrf2 signaling. (3) Autophagy pathway: the pathway can be dysregulated by the blockage of autophagosome maturation (e.g. deletion of Atg7 or Atg5) or the fusion of autophagosome-lysosome (e.g. arsenic treatment).