Fig. 1.
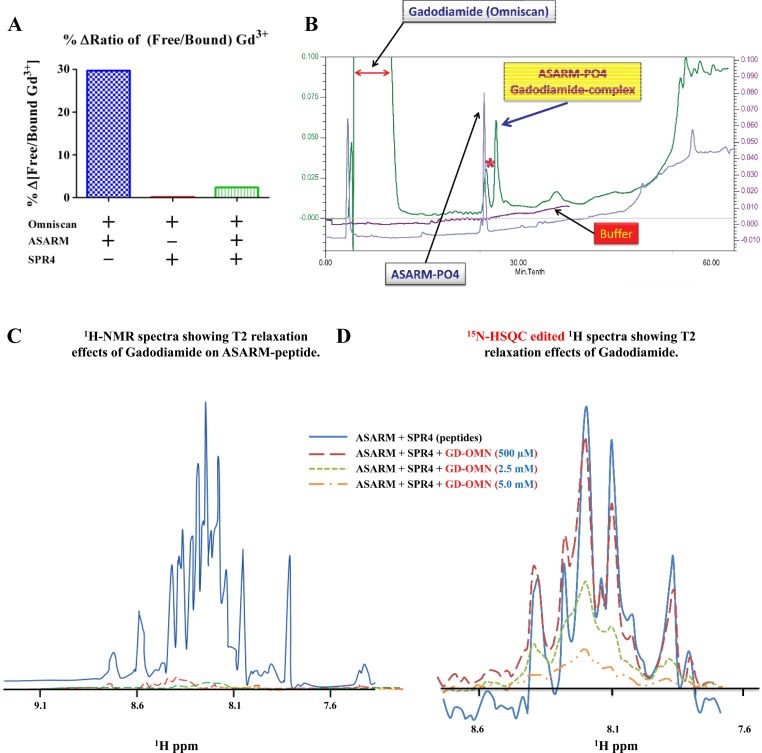
A small PHEX-related peptide (SPR4) competitively inhibits binding of Acidic Serine Aspartate Rich MEPE-associated peptides (ASARM peptides) to gadolinium (Gd3+)-based contrast agents (GBCA) in vitro. A: ASARM-induced Gd3+ release from Omniscan is prevented by SPR4 peptide. Percent change in free to bound Gd3+ in Omniscan samples treated with ASARM peptide, SPR4 peptide, or both were measured by HPLC linked to inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (HPLC-ICP-MS) in vitro. Specifically, there was a 3-fold molar excess of SPR4 peptide relative to ASARM peptide (2.9 and 0.96 M, respectively). Omniscan was added at 0.49 M; see figure for combinations. We have shown previously that this ratio of ASARM peptide to SPR4 peptide is optimal for binding in vitro and in vivo (12, 16, 18). The Y-axis represents the percent ratio difference of free to bound gadolinium relative to vehicle. The total free and bound gadolinium for control (vehicle and Omniscan) and experimental conditions were not significantly different [17,400 ppm (μg/g) SD ± 8,508]. For all experimental conditions including vehicle, we detected a significant amount of free Gd3+. The ratios of “free/bound” gadolinium for gadodiamide treated with vehicle, ASARM peptide, SPR4 peptide, and SPR4+ASARM peptide were 0.58, 0.76, 0.59, and 0.60, respectively. B: ASARM peptide binds to gadodiamide: HPLC separation of peptides on a phenomenex C18 5μ jupitor column. Traces A and D show buffer gradient profiles (buffer A; 0.1% TFA/H20, buffer B; 100% acetonitrile/0.1% TFA). ASARM-gadodiamide complex resolves from free ASARM and gadodiamide. C: our previous published studies using 2-dimensional 1H/15N nuclear magnetic resonance (2D-NMR) and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) showed ASARM peptides bind to PHEX and SPR4 in vitro and in vivo (12, 16, 18). The 1H-NMR spectra of the ASARM peptide and SPR4 peptide binding complex and the effects of gadodiamide (Omniscan) on T2 relaxation are shown. A 5.8-fold molar excess of ASARM peptide (2.73 mM) to 15N-labeled SPR4 peptide (0.48 mM) was used as previously described (12). Broadening and quenching of spectral peaks as measured using 1H-NMR even at low concentrations of Gd3+ contrast agent “gadodiamide” occurred. D: in contrast, 15N-HSQC-edited spectra of the same sample run shows vastly reduced 15N-labeled SPR4 peptide line broadening effects. For further discussion and explanation, see the text.