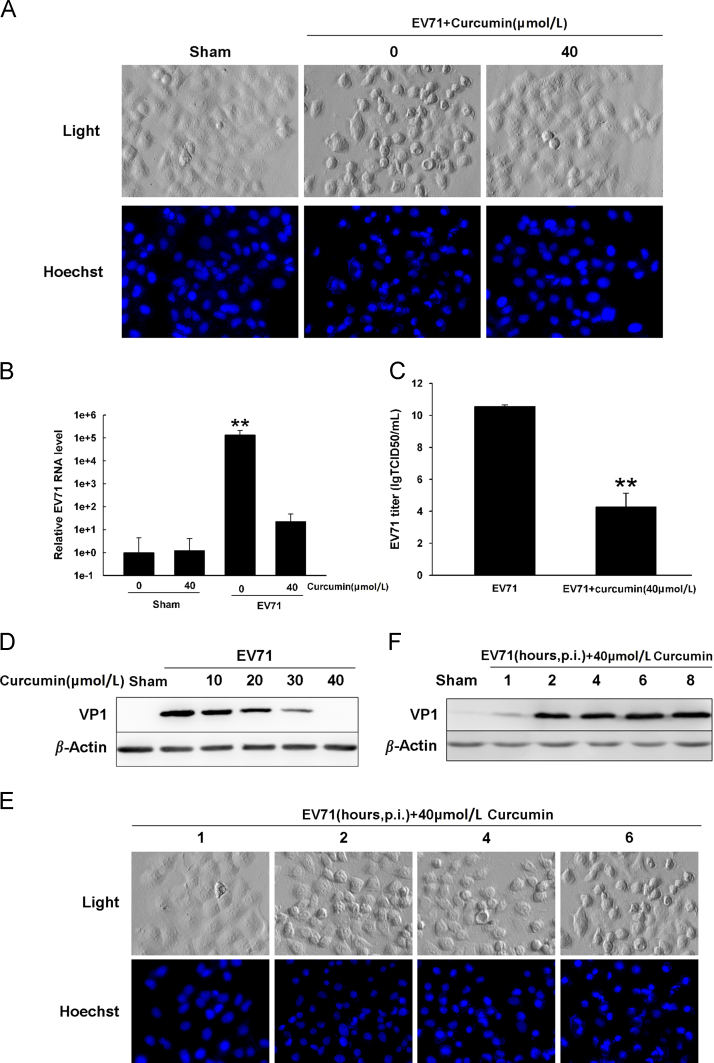
Figure 1.
Curcumin inhibits EV71 replication. (A) Cells were infected with EV71 and cultured in the medium containing 40 μmol/L curcumin for 7 h, after which were stained with Hoechst33342 to view the nuclei. (B) Cells were treated as described in (A). EV71 RNA level was determined by RT-qPCR and normalized to the RNA level of GAPDH. **P<0.01 compared with uninfected cells. (C) Cells were treated as described in (A) and virus titer was determined by TCID50. **P<0.01 compared with EV71-infected cells without curcumin treatment. (D) EV71-infected cells were treated with curcumin at various concentrations. Proteins were extracted and western blot analysis was performed with anti-VP1 antibody. (E) Cells were infected with EV71 for 8 h and curcumin was added to the culture medium at various time points after p.i. Cells were stained with Hoechst33342 to view the nuclei. (F) Cells were infected with EV71 for 8 h and curcumin was added to the culture medium at various time points after p.i. Proteins were extracted and VP1 was analyzed by western blotting. Error bars show standard deviations. n=4. Results are representative of three independent infection experiments.