Figure 8. Homeostatic mechanism of monocyte-derived eNampt-dependent biosynthesis of myocardial NAD+ in cardiac compensation to pressure overload.
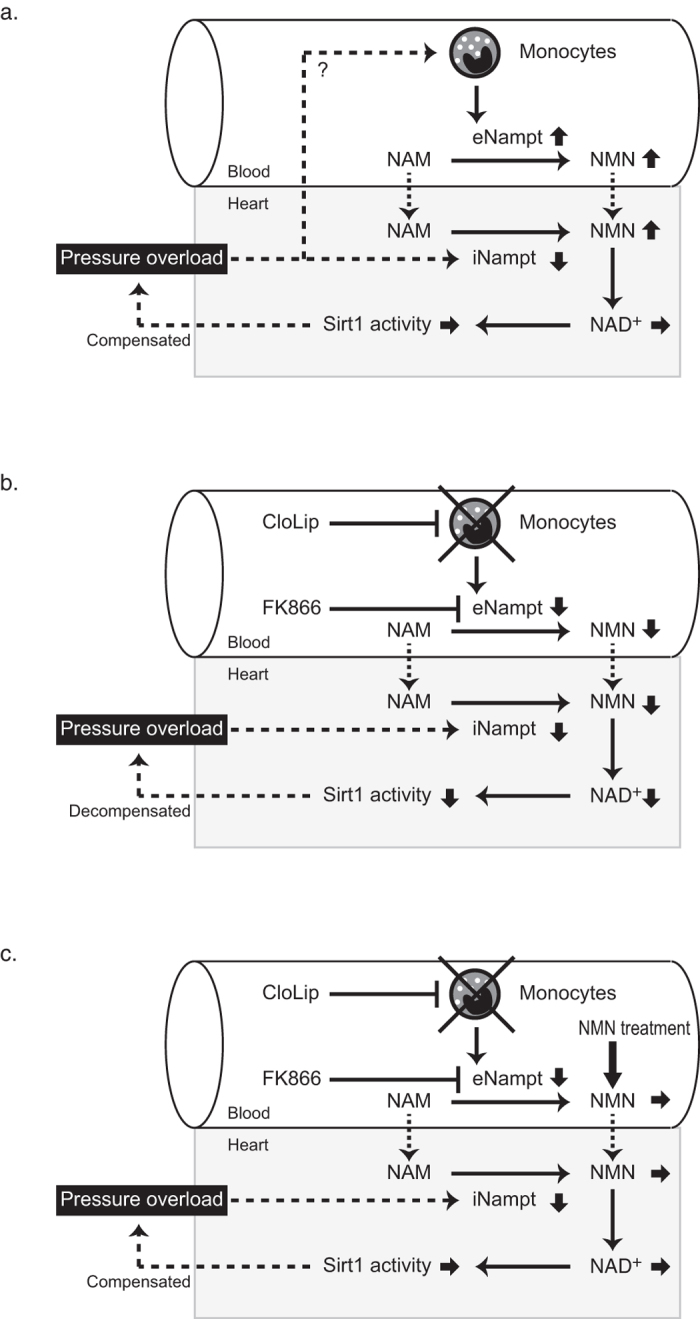
(a) Pressure overload decreases cardiac iNampt expression, but myocardial NAD+ concentration and Sirt1 deacetylase activity are unchanged. Up-regulation of monocyte-derived eNampt contributes to preservation of myocardial NAD+ levels and functional compensation to pressure overload. (b) Pharmacological inhibition of Nampt by FK866 or depletion of monocytes by CloLip suppresses compensatory up-regulation of monocyte-derived eNampt and disrupts the homeostatic mechanism of myocardial NAD+ levels and Sirt1 activity, leading to pressure overload-induced cardiac decompensation. (c) Systemic administration of NMN restores myocardial NAD+ levels and Sirt1 activity and prevents FK866- or CloLip-induced cardiac decompensation to pressure overload.
