Table 1. Size characteristics of test airborne bacterial particles.
| Bacterium | Airborne microorganisms | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GMD (μm) | Peak diameter (μm) | GSD | |
| E. coli | 0.98 ± 0.004 | 1.04 ± 0.001 | 1.24 ± 0.341 |
| B. subtilis | 0.99 ± 0.013 | 1.04 ± 0.030 | 1.26 ± 0.013 |
| S. epidermidis | 0.79 ± 0.002 | 0.84 ± 0.026 | 1.18 ± 0.001 |
The geometric standard deviation (GSD) is defined as 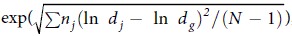 , where dj is the diameter of an individual particle, nj is the number of particles in the jth group, N is the total number of particles, and ln dg is the natural logarithm of the geometric mean diameter (GMD) of the particles, defined as
, where dj is the diameter of an individual particle, nj is the number of particles in the jth group, N is the total number of particles, and ln dg is the natural logarithm of the geometric mean diameter (GMD) of the particles, defined as 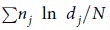 . Data are listed as the means of 10 repetitions plus/minus the standard deviation.
. Data are listed as the means of 10 repetitions plus/minus the standard deviation.
