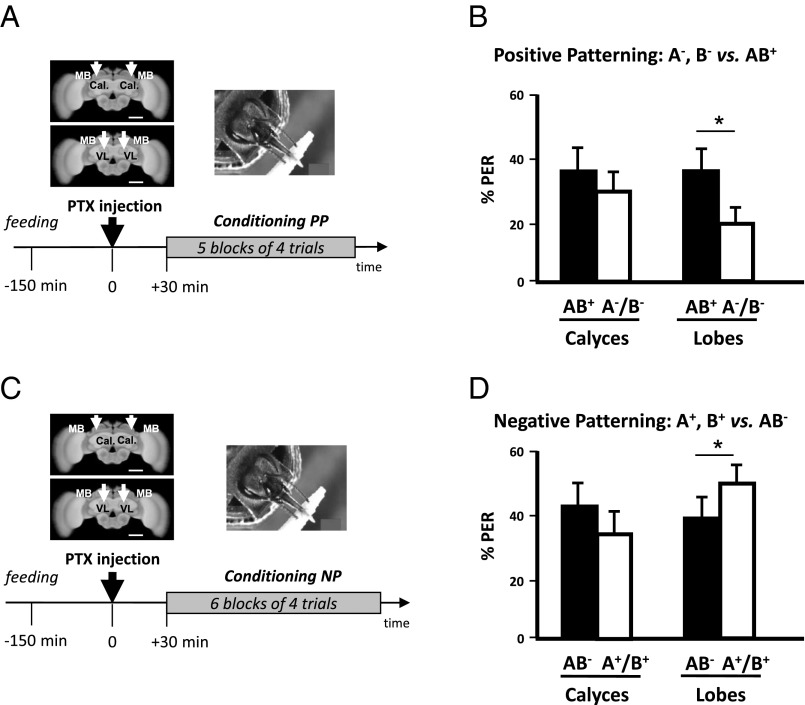
Fig. 3.
Blocking GABAergic signaling in the mushroom body calyces impairs patterning discrimination. (A, Upper Left) Frontal view of a honey bee brain. MB, mushroom body; VL, vertical lobe; Cal., calyces. The white arrows indicate the sites (VL or Cal.) of bilateral injections of the GABAergic antagonist picrotoxin. (Scale bar: 250 μm.) (Lower) Sequence of the PP experiment. The black arrow at time 0 indicates the moment of picrotoxin injection. (B) Performance (% conditioned PER) in the last (fifth) block of conditioning trials of the PP discrimination. Bees injected in the MB calyces (Left, n = 40) were unable to learn the discrimination between AB+ and A−/B−, contrary to those injected in the vertical lobes (Right; n = 39). (C) Same experiment as in A, with an NP task. (D) Performance (% conditioned PER) in the last (sixth) block of conditioning trials of the NP discrimination. Bees injected in the MB calyces (Left, n = 43) were unable to learn the discrimination between AB− and A+/B+, contrary to those injected in the vertical lobes (Right; n = 54). *P < 0.05.