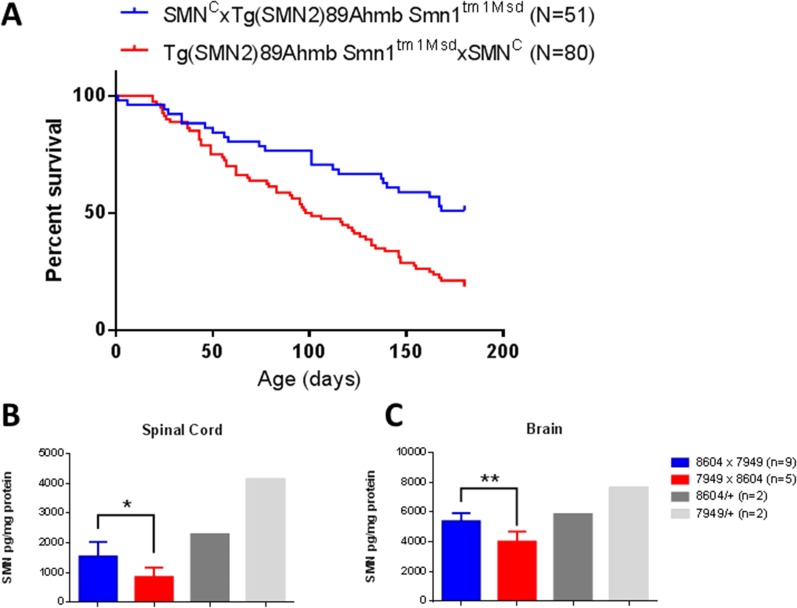
Fig. S1.
Parental genotypes affect survival and SMN levels in Burgheron mutants. (A) Survival of mutants derived from matings where the Tg(SMN2)89Ahmb transgene and the Smn1tm1Msd targeted mutation were paternally inherited and the Smn1C allele was maternally inherited was longer (P < 0.0001; Log Rank) than survival of mutants born from the reverse mating scheme. The mating scheme above the graph indicates the genotype of the parents, using the following convention: female (genotype) × male (genotype). (B and C) SMN protein measurement by ELISA in the spinal cord (B) and brain (C). Differences and significance (Student t test) between mutants inheriting the C allele (stock 8604) maternally (8604 × 7949) and mutants inheriting it paternally (7949 × 8604) are indicated. SMN levels in heterozygotes for the C allele only (8604/+) or the SMN1-targeted mutation only (7949/+) are given for reference.