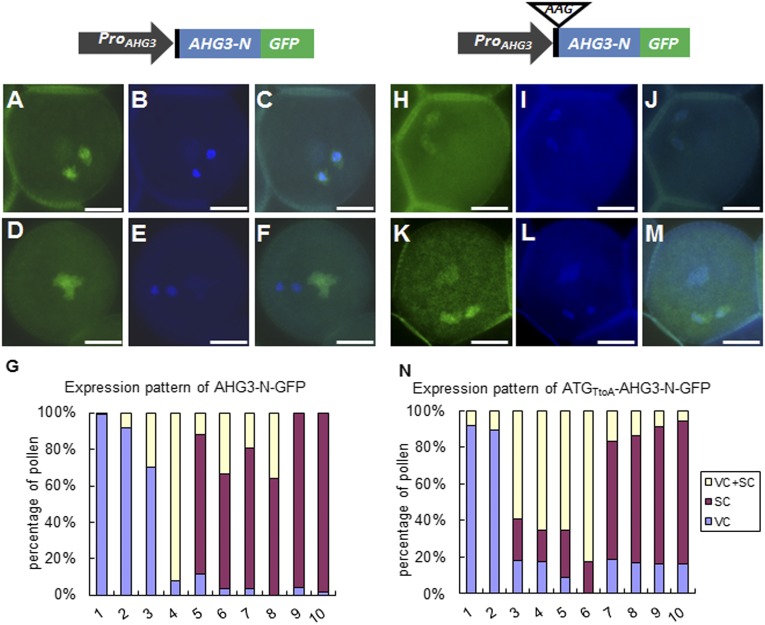
Fig. 3.
GFP localization patterns of AHG3-N-GFP and ATGTtoA-AHG3-N-GFP in mature pollen. The 5′ UTR is shown in black, GFP is shown in green, and AHG3 is shown in blue. The construct on the left contains the AHG3 native promoter driving an AHG3 genomic sequence with a C-terminally fused GFP (ProAHG3:AGH3-N-GFP); the construct on the right contains the same sequence except that the start codon in AHG3 was mutated to AAG (ProAHG3: ATGTtoA-AGH3-N-GFP). (A–F) Representative pollen grains expressing ProAHG3:AHG3-N-GFP. (A and D) GFP images. (B and E) DAPI images. (C and F) Merged GFP and DAPI images. (G) Percentage of localization patterns in pollen of 10 independent ProAHG3:AGH3-N-GFP transgenic lines. Each bar shows the distribution of localization patterns in one transgenic line. (H–M) Representative pollen grains expressing ProAHG3: ATGTtoA-AHG3-N-GFP. (H and K) GFP images. (I and L) DAPI images. (J and M) Merged GFP and DAPI images. (N) Percentage of localization patterns in pollen of 10 ProAHG3: ATGTtoA-AHG3-N-GFP transgenic lines. (Scale bars, 5 μm.) SC, sperm cells; VC, vegetative cells.