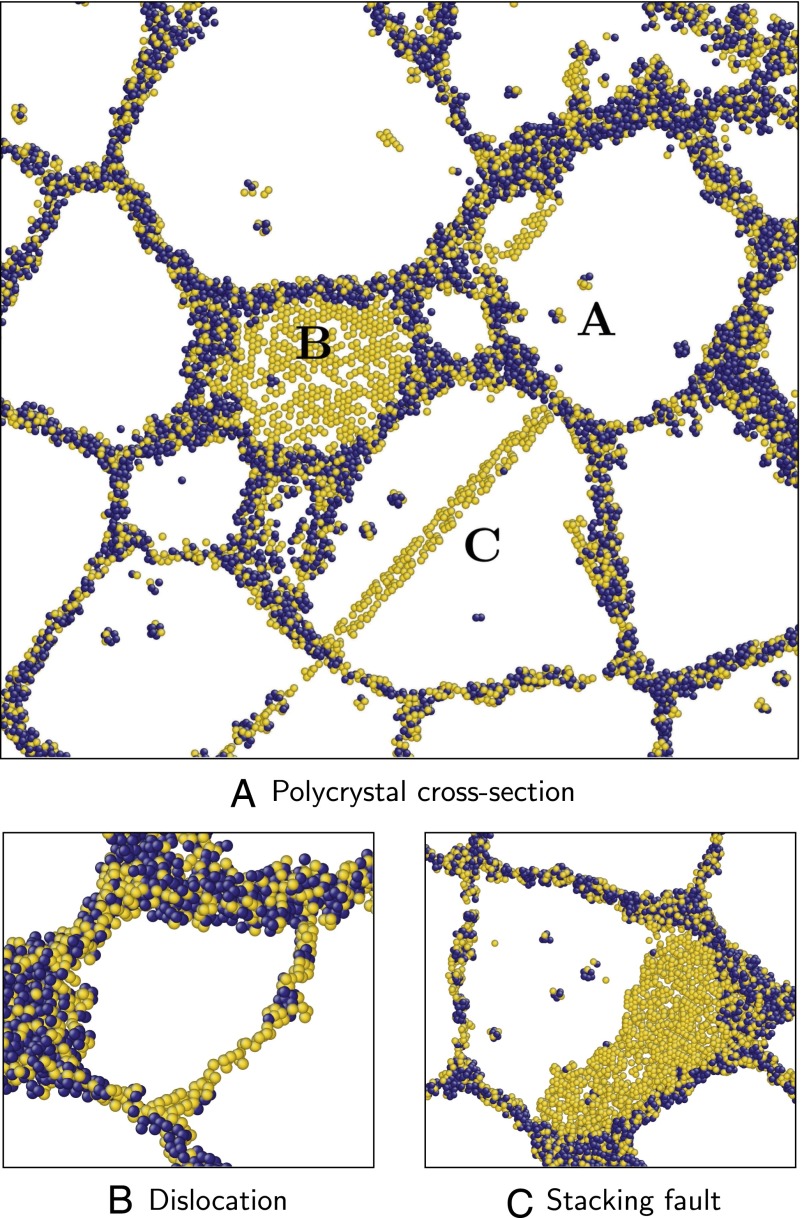
Fig. 5.
Polycrystalline aluminum at 938 K (); the width of each cross-section is 2 nm. Atoms that are FCC types are not shown for clarity. Of the ones remaining, those that are HCP types are shown in gold, and all other atoms are shown in dark blue. Grain boundaries are seen as a network of non-FCC types (dark blue and gold atoms). In cross-section A, defects are labeled as follows: vacancies, A; twin boundary, B; and stacking fault, C. Cross-sections B and C show magnified images of a dislocation and stacking fault. (A) Polycrystal cross-section. (B) Dislocation. (C) Stacking fault.