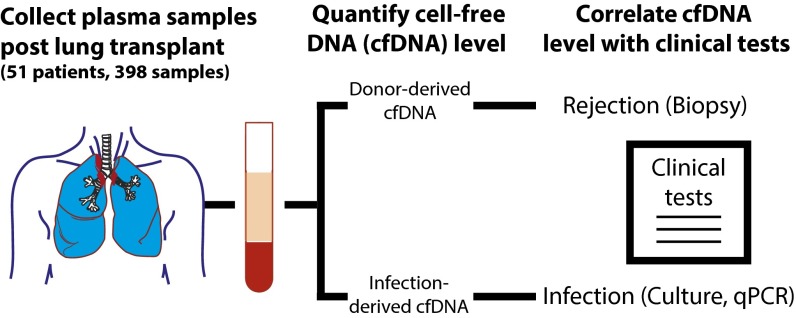
Fig. 1.
Patient recruitment, sample collection, and comparison with clinical indicators of rejection and infection. We performed a prospective cohort study to evaluate the performance of the GTD cell-free DNA assay after lung transplantation with simultaneous infection monitoring. Fifty-one patients were recruited (44 bilateral and 7 single-lung) while awaiting transplantation, and 398 plasma samples were collected longitudinally at prespecified intervals posttransplant. For each sample, human- and nonhuman-derived cell-free DNA sequences were identified and analyzed with respect to clinical metrics of graft rejection (108 transbronchial biopsies, tests of pulmonary function, and diagnosis of CLAD and AMR) and infection, respectively.