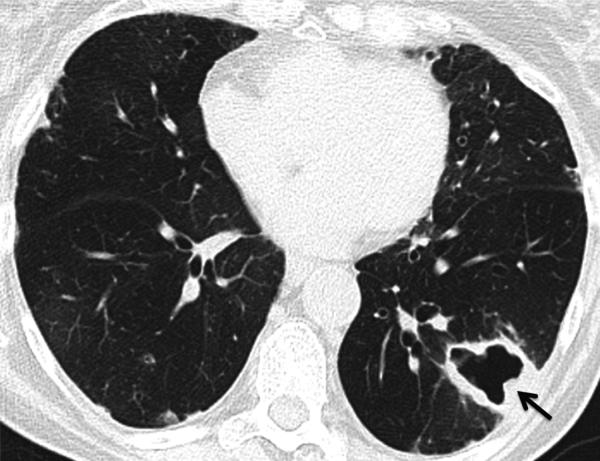
Fig. 16.
Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare (MAI) infection. CT. Thick-walled cavitary lesion in the left lower lobe (arrow) in an asymptomatic patient. Biopsy showed abscess with necrotizing granulomata and associated acid-fast bacilli. Note also mosaic attenuation suggesting air trapping, consistent with the patient's severe obstructive ventilatory deficit (FEV1 <35% predicted).
Teaching point: New large cavitary lesion in a rheumatoid arthritis patient is suspicious for infection such as tuberculosis and atypical mycobacterial infection. Multiple small cavitary nodules may be due to rheumatoid nodules, drug-related nodulosis or septic emboli.