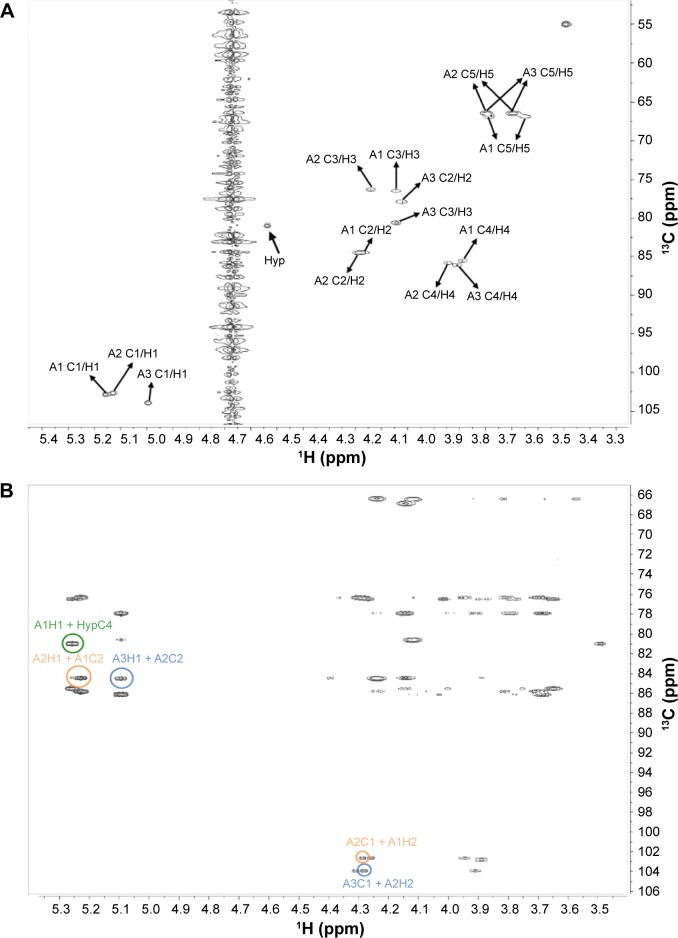
Figure 5.
Structure elucidation of RSH Hyp-Ara3. (A) HSQC spectrum: cross-peaks identified the chemical shifts of each carbon atom and its corresponding hydrogen atom(s) in each arabinose ring system. A3 is the third Ara at the nonreducing end of the Hyp-Ara3 chain, while A1 occupies the reducing end and is attached to Hyp (first Ara in the chain). A2 is the second Ara of the chain. The A1 C1/H1 label indicates the cross-peak arising from the chemical shifts of the anomeric carbon (C1) and its corresponding hydrogen (H1) on the A1 residue. The cross-peaks for the other carbon atoms and their corresponding hydrogens of A1 and the cross-peaks for A2 to A3 are similarly labeled. Two cross-peaks are observed for the fifth carbon atoms on each ring system due to their possession of two corresponding hydrogen atoms. There are overlapping signals between the cross-peaks from A1 C2/H2 and A2 C2/H2 and those from A2 C5/H5 and A3 C5/H5 due to their identical chemical shifts (Table 5). (B) HMBC spectrum: cross-peaks arising from A3H1(5.1 ppm) + A2C2(84.5 ppm) and A3C1(103.9 ppm) + A2H2(4.3 ppm), highlighted by blue circles, established the β-Araf-(1→2)-β-Araf linkage between A3 and A2; cross-peaks arising from A2H1(5.2 ppm) + A1C2(84.5 ppm) and A2C1(102.7 ppm) + A1H2(4.3 ppm), highlighted by orange circles, established the β-Araf-(1→2)-β-Araf linkage between A2 and A1, and cross-peak arising from A1H1(5.3 ppm) + HypC4(81.0 ppm), highlighted by the green circle, established the β-Araf-(1→4)-Hyp linkage between A1 and Hyp. The chemical shifts are summarized in Table 5.