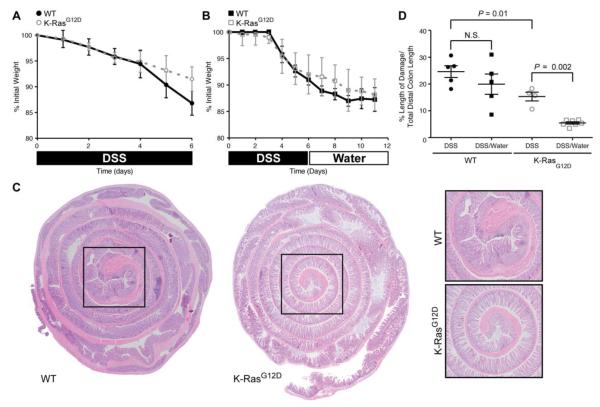
Figure 3.
K-RasG12D animals recover more efficiently from DSS-induced damage than control animals. (A) Mouse body weight changes following treatment with 3% DSS (6 days). Both experimental groups (WT, K-RasG12D) lose weight over the course of treatment, with animals expressing K-RasG12D losing slightly less weight. (B) Mouse body weight changes following treatment with 3% DSS (6 days) followed by water (6 days). Both experimental groups (WT/K-Ras) lose weight over the course of treatment. (C) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the colonic epithelium from control (WT) and K-Ras mutant animals following treatment with 3% DSS (6 days) followed by water (6 days). The epithelial damage is restricted to the distal colon (black box), which is magnified in the panels on the right. (D) Quantification of histological damage following DSS treatment (DSS). The damage was significantly reduced in K-RasG12D mutant animals both immediately after DSS exposure (P = 0.01) and following recovery from injury (P = 0.002).