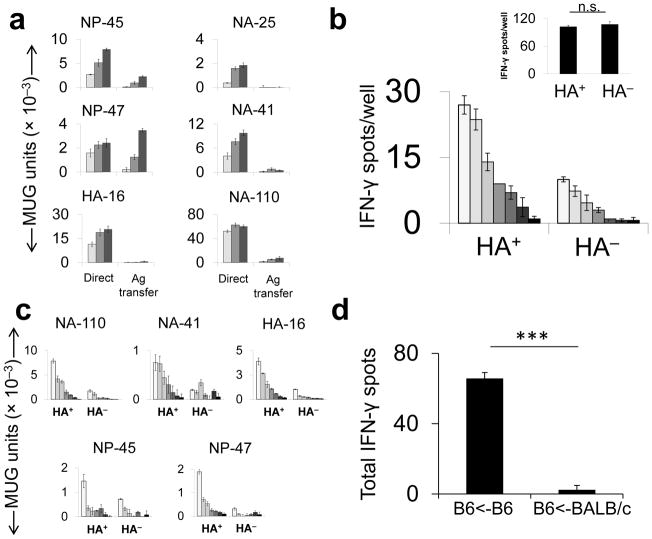
Figure 4.
Relative contributions of direct endogenous presentation and antigen transfer in vitro and in vivo. (a) MHCII− L929 cells were infected with live PR8 and co-cultured with uninfected BMDCs and T hybridomas (“Antigen [Ag] Transfer”). For the comparator (“Direct”), BMDC were pulsed with live PR8 under the same conditions as in Fig. 1b. (b) B6 mice were infected with PR8 i.n. (128 HAU) and 3 d.p.i., MHCII+ cells were isolated from homogenized lungs, flow-sorted into HA+ and HA− cell pools and combined in an ELISpot assay with PR8-immune (main panel) or vaccinia virus (VACV)-immune (inset) CD4+ T cells. Inset: The HA+ and HA− pools were pulsed with a VACV-derived peptide and co-incubated with a VACV-specific polyclonal CD4+ T cell population (c) MHCII+HA+ and MHCII+HA− cells, prepared as described in b were co-cultured with T hybridomas overnight. (d) Naive splenocytes from B6 or BALB/c donor mice were infected with 50 HAU live PR8 per 1×106 cells, cultured overnight and then UV irradiated to prevent transmission of infectious virus. B6 mice were immunized i.p with 5 ×106 infected cells. 11d later, IFN-γ-producing CD4+ T cells were quantified by ELISpot assay.
(a,c & d) representative of three and (b) two independent experiments performed in triplicate. Data are presented as mean ± s.d. Background [(a) mean uninfected APC; (b & c) MHC-II+ cells from B/Lee inoculated mice, (d) mean DMSO] was subtracted from the experimental group results.(b & d). Statistical significance was tested by one-tailed Student’s t-test.*** P < 0.0001.(d) Results with individual peptides were summed and mean standard deviation for the total was determined by calculating the square root of the averaged variances. MUG, methyl-umbelliferyl-β-D-galactoside