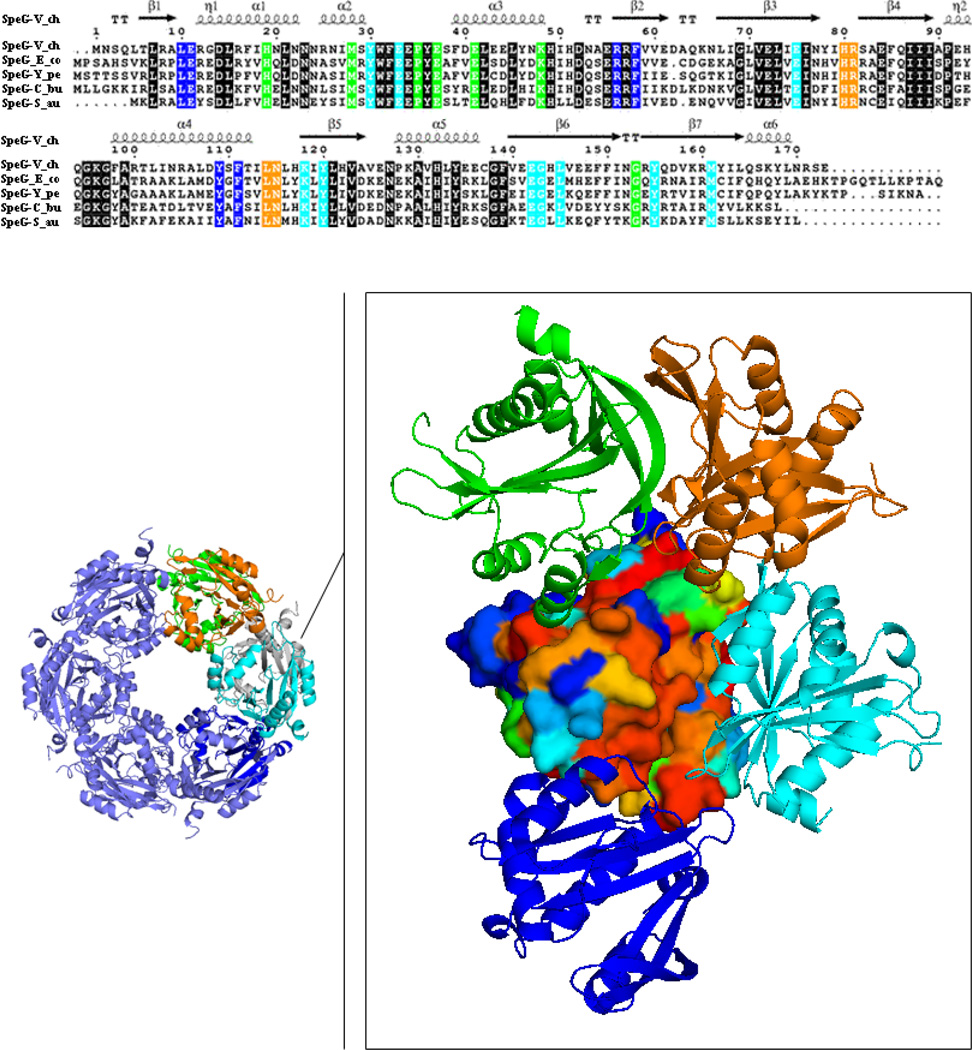
Fig. 1.
SpeG sequence-structure alignment. Surface representation of the SpeG monomer colored by degree of sequence conservation from red for 100 % conserved residues to blue for non-conserved residues. The neighboring monomers interacting with the SpeG monomer within the dodecamer are displayed as ribbon diagram and colored in cyan, green, blue and orange. Conserved residues located on the interface between contacting monomers in the SpeG dodecamer are colored according to the sequence alignment that shown on top of the figure. Sequence alignment of SpeG from V. cholerae (SpeG-V_ch) with other SpeG homologs includes: SpeG from E. coli (SpeG-E_co), SpeG from Y. pestis (SpeG-Y_pe), SpeG from C. burnetii (SpeG-C_bu) and SpeG from S. aureus (SpeG-S_au). In the sequence alignment conserved residues of the protein active site are shown on black background. Secondary structure elements of the SpeG monomer from V. cholerae are presented above the sequence. The sequence alignment of SpeG from V. cholerae with other homologous proteins was generated using CLUSTALW [48] and formatted in ESPript [49].