Figure 7.
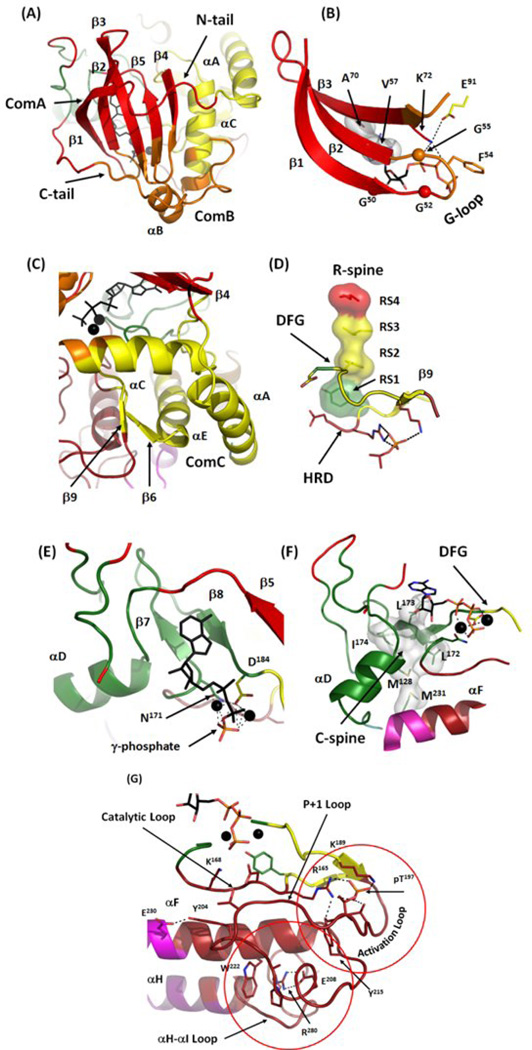
Detailed view of major communities in active PKA. (A) Community A (red) includes most of the rigid β-sheet from the N-lobe and adjacent parts of N- and C-tails. Community B (orange) includes the end of the C-tail, the αB-helix, a part of the αC-helix and two loops the G-loop and β4-β5. (B) Close-up of the community assignments around the G-loop. The three conserved glycines are shown as spheres. Most of the G-loop is associated with Community B with Phe54 facing the αB-helix. ATP binding is mostly controlled by the residues from Community A: V57 and Ala70 from the C-spine and Lys72 from the β3, but the β- and γ-phosphates of ATP, are positioned by Community B. (C) Community C (yellow) includes most of the αC-helix, a large portion of the α-E helix, the β6-β9 sheet and the N-tail of PKA with the αA-helix. (D) Community C contains elements that are the most critical for active conformation: the DFG-motif, RS3 from the αC-helix and the β6-β9 sheet. (E) Community D (green). Adenine ring and ribose of ATP are supported by the β7-β8 sheet including three C-spine residues on β7 (Leu172, Leu173 and Ile174). Community D also includes the most of important residues for catalysis and magnesium coordination, the main chain of Asp184 from the DFG-motif and Asn171 from the Catalytic Loop. (F) Most of the C-spine (white surface) is a part of the Community D. (G) Community F. This community includes the EPK-specific Activation Segment, the Catalytic Loop, most of the αF-helix and the αH-αI Loop. It is built around two conserved structural elements (red circles): the phosphorylated residue in the Activation Loop (Thr197) and the buried salt bridge between Glu208 from the APE-motif and Arg280 from the αH-αI Loop.