Figure 2. Schizophrenia patients show decreased left-hemispheric and increased right-hemispheric specialization of the caudate nucleus.
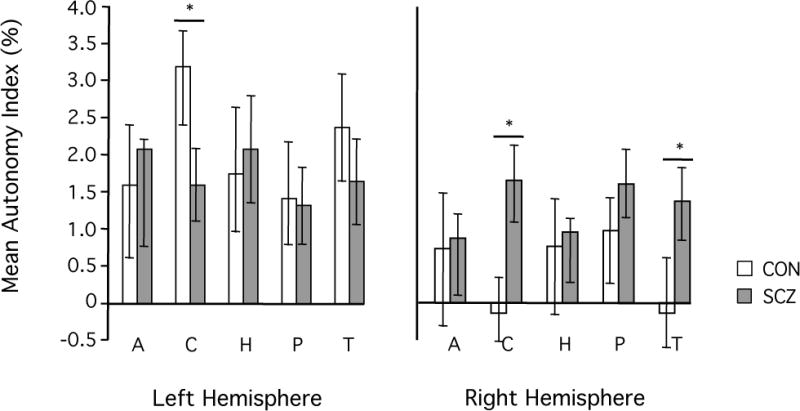
AI values were averaged within five subcortical regions, including two striatal structures (caudate nucleus and putamen), two limbic structures (hippocampus and amygdala), and the thalamus. Bars represent the mean AI value across subjects with the respective subcortical structure. Error bars indicate two standard errors. In the healthy control group (white bars) AI values were generally higher in the left than in the right hemisphere. In the patient group (gray bars) this overall pattern was generally less pronounced. Specifically, schizophrenia patients exhibited significantly decreased left- but increased right- hemispheric specialization of the caudate nucleus as compared to the healthy controls (p<0.005, respectively).
