Figure 3. Schizophrenia patients show segregated left-hemispheric and right-hemispheric networks connected to the caudate nucleus and the putamen.
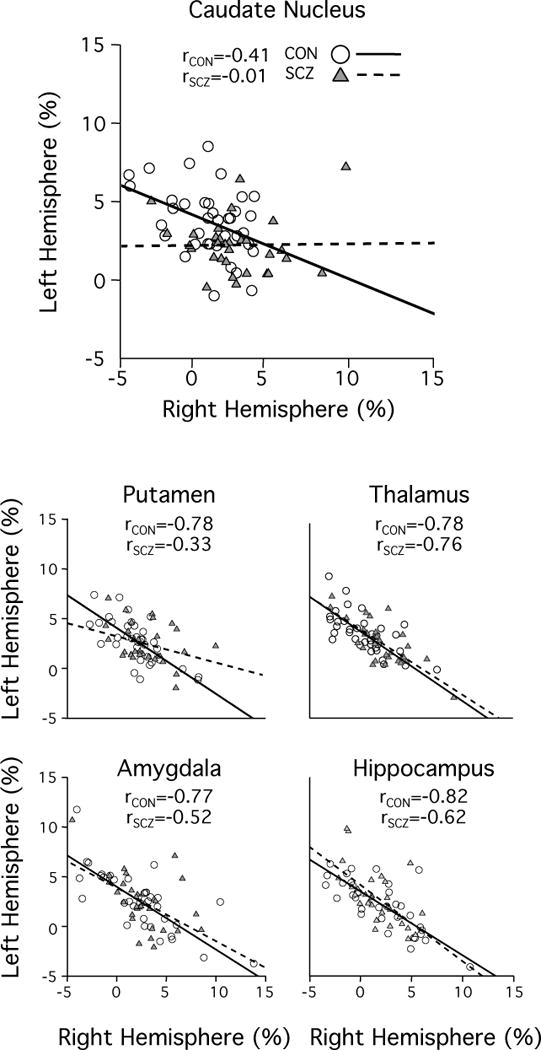
According to the mathematical definition of the autonomy index, for a specific network spanning across two hemispheres, a negative correlation between left and right hemispheric AI values should be expected. All subcortical structures of interest showed this strong negative correlation in the healthy control group (solid line, white circles). In schizophrenia patients, this characteristic anti-correlation was reduced in the caudate nucleus and the putamen as compared to their healthy controls (dotted line, gray triangles), indicating a disruption of interconnection and coordination between the two hemispheres.
